Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
TABLE 8.2 Summary of Several Important Reactions Involving NO
x
in
Hydrogen Combustion
NO formation
1. N
2
O
+
O
=
NO
+
NO
2. NNH
+
O
=
NH
+
NO
3. N
+
O
2
=
NO
+
O
4. N
+
N
2
=
NO
+
N
5. N
+
OH
=
NO
+
H
NO removal
6. NO
+
HO
2
=
NO
2
+
OH
7. H
+
NO
+
M
=
HNO
+
M
8. NH
+
NO
=
N
2
O
+
H
9. N
2
H
2
+
NO
=
N
2
O
+
NH
2
Other reactions
10. N
2
O
+
M
=
N
2
+
O
+
M
11. N
2
O
+
H
=
N
2
+
OH
12. N
2
O
+
O
=
N
2
+
O
2
13. NO
2
+
H
2
=
HONO
+
H
Note
: M for nonreactive gas such as N
2
, Ar, or He.
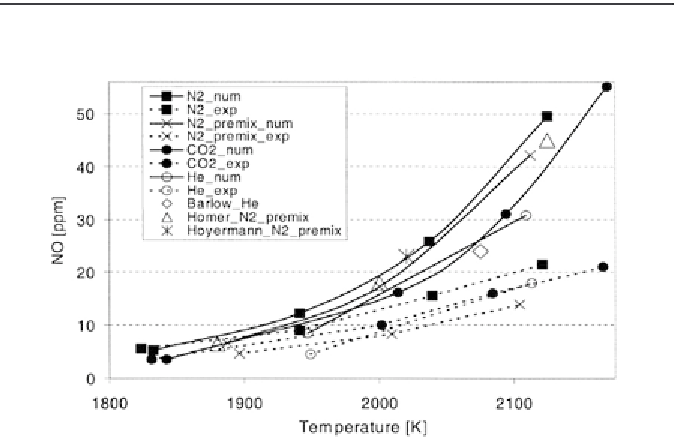
FIGURE 8.3
Dependence of maximum [NO] on maximum temperature for different experimental
results and numerical simulations [6].
Dilution with gases such as N
2
reduces the flame temperature and thus
the thermal mechanism of NO
x
formation. At high dilutions, the thermal
mechanism is almost suppressed and the NO
x
formation occurs mainly
through NNH and N
2
O mechanisms [5].
NO
x
emission from hydrocarbon combustion is strongly influenced
by hydrogen addition. For example, in a recent study of mild flameless
Search WWH ::

Custom Search