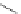Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
N
R
I
R
R
I
2
N
N
N
a
: R = H (74%)
b
: R = Me (71%)
N
acetone
reflux
EtO
N
N
N
R
I
Scheme 3.11
Synthesis of cyclic amidines from imidate and aziridines
sulfonamide by treatment with
-bromoorthobutanoate followed by azidation and reduc-
tion. These bisamidines are used as chiral ligands for the copper-catalysed enantioselective
Diels-Alder reaction [24a].
Bicyclic amidines are synthesized from aziridines and cyclic imidates [25]. Thus, NH-
aziridines react with cyclic imidates in the presence of a small amount of ammonium
bromide to give aziridinylamidine, which is treated with iodine (I
2
) to give bicyclic
amidines. The use of 2-methylaziridine results in the introduction of methyl group at
position 2 of the bicyclic amidine product. The mechanism proposed is shown in
Scheme 3.11, which involves iodine-induced ring opening of aziridine and recyclization
of the resultant iodoethylamidine.
g
3.2.4.3 Haloiminium Salt
One-step conversion of N-(
o
-azidoalkyl)lactams to bicyclic amidines, avoiding the protec-
tion-deprotection sequence on the amine part, is explored by applying the intramolecular
Staudinger-type reaction [26]. Oxalyl chloride [(COCl)
2
] and bromide [(COBr)
2
] are found
to be effective trigger reagents and the corresponding bicyclic amidines are produced in high
yield (Table 3.1).
DBN (2) is prepared in 92% yield by treatment of N-(3-azidopropyl)-
-lactam with
oxalyl bromide after quenching with anisole (run 3). A trace of the reaction by IR spectrum
suggests the formation of a bromoiminium intermediate, which spontaneously cyclizes to
the bicyclic system through either 1,2-addition (path A) or [3
g
þ
2]cycloaddition (path B)
(Scheme 3.12).
Table 3.1
Synthesis of DBN (2) from N
-(3-azidopropyl)-
g
-lactam
N
3
N
O
reagent
N
N
solvent
DBN (
2
)
Run
Reagent
Solvent
Yield (%)
1
Ph
3
PorBu
3
P
xylene
<
10
2
(COCl)
2
DCM
81
3
(COBr)
2
(CH
2
Cl)
2
92