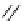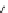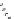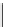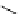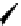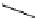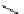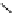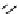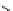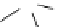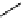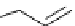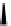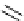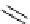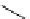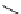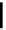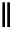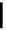Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
BIM
HN
BIM
BIM
NH
R
2
O
R
2
O
Base
N
Base
O
NH
O
O
-
R
1
OH
+
O
O
O
P
O
OH
H
2
O
P
OR
1
O
-
O
RNA
N
BIM =
N
H
H
N
R
N
N
H
H
O
O
P
Osugar
R
1
O
recognition of phosphate
Scheme 9.5
Guanidine catalysed hydrolysis of RNA
Mechanistic approaches to the (thio)urea catalysed Strecker reaction by NMR analysis
and theoretical calculations [27] reveal that: the catalyst has a stable 3D structure and
isomerises the E-imine substrate to a Z-one; only the hydrogen of the (thio)urea interacts
with the Z-imine through double hydrogen bonding; and the double interaction changes to a
single one during the reaction, in which the bond strength is weakened and the liberated
(thio)urea can be recycled (Scheme 9.6).
Thiourea effectively catalyses hydrophosphorylation of imine [28] (Table 9.10). The
products can be deprotected under mild hydrogenolysis conditions to afford the corre-
sponding optically active amino phosphoric acids.
R
2
t
Bu
X
N
R
1
N
H
N
H
sterically
demanding
groups
O
N
HO
R
1
, R
2
= H, Me, or Bn
R
3
= Bn or OCO
t
Bu
X = O or S
t
Bu
R
3
Figure 9.8
Sterically demanding groups of aryl thioureas