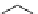Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
O
O
O
Ar
Ar
Ar
Ar
A
N
N
N
N
Ar
Ar
N
N
+
HH
A
HH
A
HH
proton acceptor
bisarylurea
double hydrogen
bonding
single hydrogen
bonding
O
Ar
Ar
N
N
HH
O
Ar
Ar
N
N
HH
self recognition
(b)
NO
2
NO
2
O
O
O
HH
Ar
Ar
Ar
Ar
Ar
Ar
O
N
N
N
N
N
N
HH
O
X
HH
O
HH
OO
X
N
HH
N
RR
A
Figure 9.3 (a) Types of coordination of urea through hydrogen bonding; (b) counter part in
double hydrogen bonding
On the other hand, inverse affinity between thiourea and urea is reported in the
complexation with sulfonate, in which great improvement in the affinity is also observed
in the nitro-substituted arylurea derivatives [16] (Table 9.4).
9.3.2 Urea and Thiourea Catalysed Reactions
It was reported by Curran et al. [19] in 1994 that a symmetrical N,N
0
-diarylurea effectively
catalyses the allylation of cyclic sulfinyl radicals with allyltributylstannane (Table 9.5).
High trans selectivity in the product was observed when a stoichiometric amount of urea
catalyst was used (run 4), suggesting activation in the transition state by double hydrogen
bonding between the urea hydrogen atoms and the sulfinyl oxygen atom.
Catalytic activity of the same urea and its variations was examined in the Claisen
rearrangement of 3-methoxyvinyl vinyl ether [20] (Table 9.6). Great rate acceleration was
observed in the use of thiourea, even though completion of reaction could not be estimated
due to slow decomposition of the catalyst under the reaction conditions used (run 6).