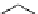Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
(b) Chemical reaction :
metal catalysis
(a) Enzymatic reaction
highly specific
and
efficient reaction
Lewis acid
activation
ML
n
H
H
Y
Y
S
R
S
R
S
R
S: substrate
R: reactant
ML
n
= metal catalyst
Enzyme
(c) Chemical reaction: metal-free catalysis
i.
ii.
X
X
N
HH
N
N
HH
N
R
1
R
2
R
1
R
2
-
O
Y
Y
S
R
S
R
Lewis acid like activation
recognition and activation
double hydrogen bonding
X = O (urea), S (thiourea), NR
3
(guanidine);
Y = hetero atom R
1
, R
2
, R
3
=H, alkyl, or aryl
Figure 9.1
Schematic paths of catalytic reactions
participate. Furthermore, structurally related urea and thiourea compounds are now well
developed as alternative organocatalysts [2-5]. In this chapter, reactions catalysed by urea
and thiourea will be discussed, mainly focusing on molecular recognition through double
hydrogen bonding.
9.2 Bisphenol as an Organoacid Catalyst
9.2.1 Role of Phenol as Hydrogen Donor
Hine et al. [6] approached the complex structures of bisphenol (dibenzocyclobutane-1,8-
diol) and sp
2
oxygen bearing partners using X-ray crystallographic analysis; the two