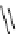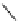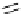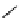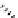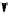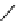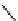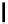Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
CO
2
Bn
CO
2
Bn
O
O
N
N
H
DAST
CH
2
Cl
2
H
N
NH
HO
O
-78 °C
O
N
Boc
N
N
Boc
N
Me
Me
Me
Me
O
O
H
H
O
O
122
BrCCl
3
CH
2
Cl
2
, rt
DBU (
1
)
S
CO
2
Bn
O
N
O
O
Me
N
N
N
O
N
N
N
O
O
Me
N
N
N
Boc
N
O
N
Me
Me
O
O
H
O
O
123
telomestatin (
124
)
71% (2 steps)
Scheme 7.27
Synthesis of telomestatin (124)
reaction promoted by guanidine base. Reaction of activated aryl fluoride 158 and naphthol 159
using Barton
sbase5 provided dinaphthyl ether 160 in 85%yield [49]. The aryl ether underwent
oxidative spirocyclization with PhI(OAc)
2
to give 161, which represents the mother skeleton of
palmarumycin CP
1
(162) and diepoxin
(163) (Scheme 7.36).
A phosphazene base catalysed S
N
Ar reaction for biaryl ether synthesis was reported by
Ebisawa et al. [50]. Reaction of activated fluorobenzoate 164 and functionalized phenol
165 with TMSNEt
2
and a catalytic amount of phosphazene of P4-
t
Bu (10mol %) gave
biaryl ether 166 in 94% yield. The biaryl ether was efficiently led to dictyomedin A (167)
and B (168) (Scheme 7.37).
The aziridine ring opening reaction with phenol derivatives using copper(I) acetate
(CuOAc)-DBU was reported by Li et al. [51]. Reaction of ethynyl nosyl-aziridine 170 and
b
s
-hydroxytyrosine derivative 169 in the presence of DBU (2 equiv.) and a catalytic amount