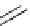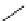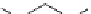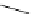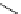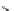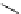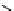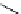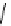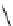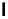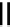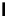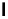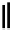Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
Pd (OAc)
2
(1.5 mol%)
ligand (3-6 mol%)
Br
+
K
2
CO
3
(3 mmol)
(HO)
2
B
MeO
MeO
MeCN
(1.2 mmol)
(1 mmol)
ligand
NH
NH
NR
NBu
Me
Me
Me
R
Me
Me
Me
N
N
N
N
R
N
N
N
Me
N
Me
R = Me (74%)
R = Et (78%)
R = Bu (81%)
Me
Me
R = Bu (99%)
R =
s
Bu(100%)
R =
t
Bu (100%)
n
(98%)
n = 1 (83%)
n = 2 (80%)
none (42%)
Scheme 4.35
Screening of the guanidine ligands on the Suzuki coupling reaction
with a wide range of aryl halides in aqueous solvent to give the coupling products in good
to excellent yields and high turnover numbers. 1-Iodo-4-nitrobenzene was reacted with
phenylboronic acid to afford biphenyl in 85% and its turnover number was high (up to
850 000). Results for the preliminary screening of the guanidine ligands in the reaction of
1-bromo-4-methoxybenzene and phenylboronic acid are summarized in Scheme 4.35.
Barton
s bases were found to be the best ligands, which gave the coupling product in
nearly quantitative yield.
The Heck reaction of olefins with aryl halides proceeds successfully in the presence of
palladium catalyst supported on TMG (1) modified molecular sieves without solvent. The
TMG-Pd was found to be much more active and stable than the palladium catalyst without
modification with TMG (1) [87]. An ionic liquid, tetramethylguanidinium lactate, was used
as the TMG source.
Zinc
Chiral zinc-guanidine complexes were designed as possible chiral auxiliaries in organic
synthesis [88]. TMG (1) was successfully reacted with diethylzinc (Et
2
Zn) in a 4 : 3 and a
1 : 1 ratio to yield the corresponding linear [Zn
3
(
-TMG)
(Et)]
3
complexes. The cyclic complex was further reacted with alcohol and/or phenol to
give alternative complexes such as 21, which can catalyse the ring-opening polymerization
of lactide into poly-lactide [89] (Scheme 4.36).
m
-TMG)
4
(Et)
2
] and cyclic [Zn(
m
4.3.3.4 Oxidation
Tetraphenylbismuth trifluoroacetate under neutral or slightly acidic conditions phenylates
primary alcohol in reasonable yields (65-75%), but gives only moderate yields with
secondary alcohols. In contrast, the reaction of bismuth [Bi(V)] reagents with alcohols
under basic conditions [BTMG (2)orTMG(1)] gives, exclusively, oxidation [90].