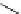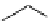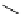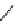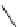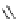Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 4.13
TMG (1) assisted
a
-alkenylation of
b
-keto esters with bismuth reagents
(4-MePh)
3
Bi
+
R
3
R
2
R
2
BF
4
-
CO
2
Et
R
1
R
1
R
3
CO
2
Et
TMG (
1
)
PhMe, -50 ºC to rt
O
O
R
1
R
2
R
3
Run
Yield (%)
1
-(CH
2
)
4
-
n-C
6
H
13
86
-(CH
2
)
3
-
)
(
90
2
3
a
Me
H
96
Ph
4
Me
Me
90
a
2 Equiv. of the bismuth salt/TMG (
1
) were used.
nation with a Barton base allows a general purification-free HWE synthesis of
a
,
b
-
unsaturated esters and nitriles from both aromatic and aliphatic aldehydes.
4.3.3.3 Metal Mediated Reaction
Bismuth
TMG (1) assisted alkene transfers from alkenyl bismuth reagents to reactive electrophiles
have been reported [83]. Treatment of
-diketones and phenols with
alkenyltriarylbismuthonium salts in the presence of TMG (1) smoothly affords
b
-keto esters,
b
a
-alkeny-
lated products [83b] (Table 4.13).
Palladium
An organobase including guanidine is often used as co-catalyst (or base) in palladium
coupling reactions [84]. The 2-methylenepropane-1,3-diol diacetate reacts with 7,8-
dihydroquinoline derivative in the presence of palladium acetate [Pd(OAc)
2
], TMG (1)
and triphenylphosphine (PPh
3
) to give the methylene bridged compound in 92% yield,
which can be converted to a diamino analogue of huperzine A, an inhibitor of acetylcholine
esterase [84a](Scheme 4.32).
O-Allylic urethanes and carbonates are afforded from amines/alcohols, carbon dioxide
and allylic chlorides by palladium catalysed reaction in the presence of an organobase. The
choice of added base in the generation of carbamates/carbonates was critical for high yields
Me
H
N
OMe
AcO
OAc
N
N
O
OMe
Me
HO
O
Pd (OAc)
2
, PPh
3
NH
2
CO
2
Me
CO
2
Me
TMG (
1
)
huperzine A
92%
Scheme 4.32
TMG (1) catalysed palladium coupling reaction