Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
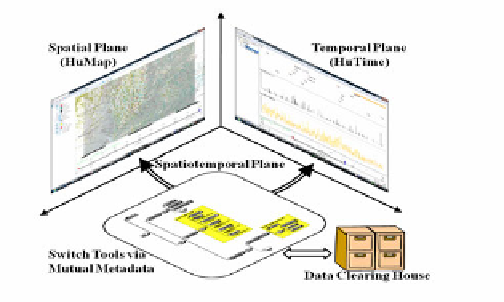
specification of a spatiotemporal tool. Internal data structures of HuMap and HuTime
are not identical due to different development backgrounds, which make data
exchange between two tools difficult. To solve this problem, a mutual metadata is
defined. Just like a pipeline, data are exchanged via this metadata. This switching
function will be realized within this year. These flexible developments are possible
because all tools are programmed and owned by the H-GIS. This is the reason why
the H-GIS has developed all systems and tool by itself.
Fig. 10.
Schematic Specification of a Spatiotemporal Tool
Accumulations of data whose semantics and spatiotemporal attributes are well
organized are essential in order to fully use spatiotemporal tools. An RSS is a solution
to this problem, and several systems are in operation. Two challenges now remain to
be faced. One is to introduce ontology technology. Since area studies are collection of
many disciplines, a given word in a discipline not always has the same meaning in the
other discipline. Vocabularies should be organized by meaning so that computers can
process them, allowing information retrieval from a wide range of databases.
The second challenge is to expand and refine the spatiotemporal attributes of
metadata. The NIHU RSS uses DCMES. DCMES is simple but does not allow precise
description of spatiotemporal information. The NIHU RSS expands DCMES to
describe spatiotemporal information precisely. However, this makes the metadata
different from that of standard DCMES and difficult to link with other RSSs. The
CIAS RSS uses a combination of MODS, EAD and METS. These metadata are good
enough to describe precise information. However, there are several ways to describe
the same piece of information, which decreases retrieve abilities between other RSSs.
Spatiotemporal informatics in area studies has almost accomplished its initial step.
To make next progresses, the H-GIS is trying to set up interdisciplinary research
projects to collect, organize, analyze and integrate a variety of data sets using RSSs
and spatiotemporal tools. Evaluations, requests and opinions are being fed back from
researchers, which will be the hints for further developments. Concurrently, the H-
GIS is preparing for compiling thesauri of several disciplines related to area studies,
which will be used for intelligent data processing.
Acknowledgement.
This research was conducted by the H-GIS research group. Special thanks
are due to Prof. Mamoru Shibayama, Prof. Tatsuki Sekino and Prof. Masatoshi Kubo for
helpful discussions. This research has been supported partly by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific