Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Basic Viewer Functions
x
Arrange/display various data by place and time
x
Use maps whose coordinate systems are different simultaneously
x
Multi-format: ESRI shape file, CSV, XML metadata, JPEG, JPEG2000 etc.
x
Layer selection, change layer order, create new layers, delete layers etc.
x
Change symbol/color/size/α-value of an object (feature)
x
Zoom-in/out by place and time
x
Import/export layer data
x
Web-link
x
Put and retrieve annotations on layers
Functions as a Spatial Tool
x
Link with the data clearing house
x
Retrieve objects (features) by place, time, and subject
x
Choropleth Map
x
Animations/tracking
x
Logical operations between layers (Intersection, Union, Merge etc.)
x
GIS functions (Dissolve, Buffering, Clipping, Tracking etc.)
x
JAVA and R plug-ins for advanced analysis (under construction)
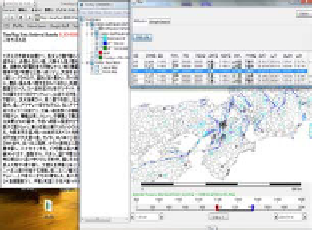
Data visualization is the basic use of HuMap. A typical view of HuMap is shown in
Figure 5 (a). Main layers of the view are political-boundaries (polygon features),
seismic active-faults (line features), and earthquake-events (point features) that are
reconstructed from historical resources about earthquakes. We can see the spatial
relationships between active faults and earthquake-events. Spatiotemporal queries are
important function of HuMap that is used to select objects within the particular area
and period. The upper-right table in the figure shows the result of the query to choose
earthquake-events during 1000 AD to 1500 AD in Kyoto area. HuMap also has a
Web-link function to link an object and its related information on the Web using
URLs. The left side text box in the figure shows the linked document of an
earthquake-event in the full-text database.
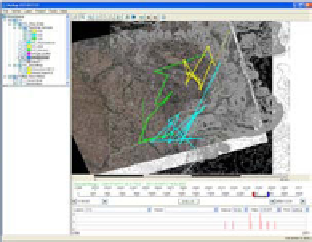
HuMap can carry out basic logical operations between layers and some spatial
operations such as dissolve, buffering, clipping, tracking, etc. Figure 5 (b) is the
example of tracking to analyze the movement of objects according to time.
(a) (b)
Fig. 5.
Example Displays of HuMap:
(a) is a typical view of HuMap and example of
spatiotemporal query, and (b) is an example of tracking analysis