Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
OH
N
OH
O
N
HO
N
OH
OH
P
O
O
O
O
O
N
OH
O
OH
O
N
O
O
O
O
PCBSD
C60-SAMs
O
O
S
n
n
N
+
Br
-
N
+
Br
-
P
3
PHT
+
Br
-
Br
-
PCBM-S
FPQ-Br
N
+
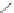
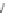
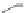
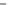
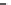
Scheme 3.4
Chemical structures of organic materials used in ETL for inverted polymer solar
cells
P3HT:PC
61
BM instead of the commonly used chlorobenzene or dichlorobenzene
to make the vertical phase segregation of donor and acceptor more favorable for
inverted devices. Like in the case of conventional devices, controlling the bulk
blend vertical phase segregation is also important in inverted devices; however, the
optimal phase segregation is different from the case of conventional devices [
84
].
3.3.1.2 Metal Oxide Nanoparticle Layer
One of the problems of sol-gel process of ZnO and TiO
x
is that they require high
temperature annealing processing conditions in order to improve the crystallinity of
the material to minimize resistive losses in the solar cell devices. These high
temperature processing conditions can reach as high as 500 C, which is not
compatible with industry scale roll-to-roll process. To overcome this problem, ZnO
NPs are introduced as ETL materials for inverted solar cells [
41
,
103
]. The devices
fabricated from the ZnO NPs on ITO-coated glass show an average PCE of
*3.6 %. This value is very similar to that obtained from the high temperature
processed ZnO sol-gel devices on glass/ITO which show an average efficiency of
*3.5 %. This demonstrates that sol-gel ZnO and ZnO NPs thin film layers can
both act as a good electron selective layer in the inverted device architecture.



















































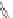
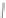





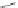

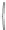
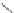








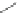

















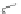































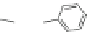

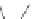




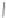
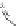














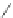







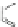

















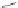




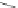
























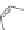



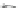

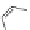

















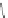


















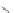


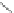
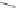
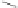












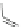

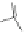






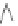






























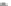



















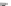




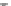








































Search WWH ::

Custom Search