Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
feedstock species. For example, bisulfite of about 8% is required for softwood, whereas only 2-4% is
required for hardwood. Cellulose-to-glucose conversion over 90% can be easily achieved even for soft-
wood with low enzyme loading. The pretreatment is directly applied to wood chips without further size
reduction. Furthermore, size-reduction energy consumption after pretreatment was only 20-50 Wh/kg
oven-dried wood (Zhu et al. 2009; Zhu et al. 2010). With excellent cellulose conversion and very low
size-reduction energy consumption, SPORL fits the requirement for forest biomass conversion. SPORL
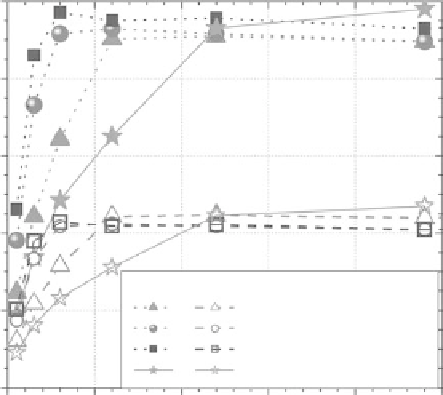
(a)
Conversion
Glucose yield
SPORL, bisulfite = 8%, acid = 3.68%
Dilute acid, acid = 3.68%
OrganoSolv-B (pan 2005)
OrganoSolv-A (pan 2005)
Red pine
Red pine
Mixed softwood
Mixed softwood
100
100
80
80
60
60
40
40
20
20
0
10
20
30
40
50
Enzymatic hydrolysis time (hour)
(b)
100
100
80
80
60
60
40
40
ECCS
EHGY
pH
4.46 0
0.92
1.84
Organosolv (pan 2006)
Acid (%)
20
20
2.32
2.00
0
0
0
10
20
30
40
50
Enzymatic hydrolysis time (hour)
FIGure 15.6
Comparison of enzymatic hydrolysis cellulose conversion and glucose yield between sulfite
pretreatment to overcome recalcitrance of lignocellulose (SPORL) and the organosolv processes: (a) softwood
and (b) aspen.