Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
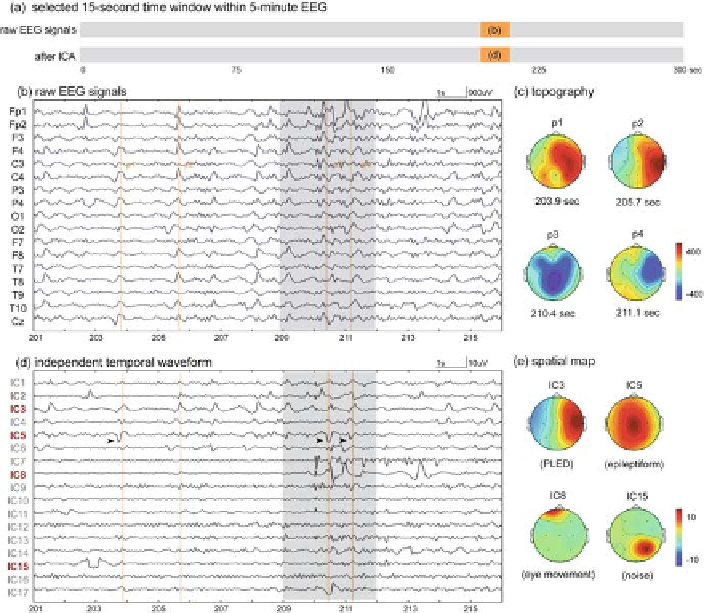
Fig. 4.4: The third selected EEG segment and ICA results from patient 1. (
a
)The
15-s time window (201-216 s) used to display results in (
b
) and (
d
). (
b
) The illustra-
tion of a 15-s segment where signals in the
shaded areas
were severely contaminated
by large eye movements and environmental noises. (
c
) The topographical maps gen-
erated at four peak time points p1, p2, p3, and p4 (
vertical lines
in
b
) of four waves
in IC3 at 203.9, 205.7, 210.4, and 211.1 s. (
d
) The 17 decomposed ICs show that
diseased-related patterns were PLEDs (IC3) and epileptiforms (IC5) and the arti-
facts were eye movements (IC8) and noise (IC15). (
e
) The corresponding spatial
maps of IC3, IC5, IC8, and IC15.
4.2 Patients and EEG Recordings
Five patients (all male) with sporadic CJD, aged 73, 74, 85, 52, and 80 years old
were recruited in this study (for details, see Table 4.1). All of them met the criteria
of probable CJD defined by WHO, were examined by board-certified neurologists,
and underwent extensive diagnostic workups, including clinical, neurophysiologi-
cal, neuroradiological examinations, and the CSF analysis. Disease onset was deter-
mined retrospectively based on history and clinical presentations as reported by the
patients themselves and their relatives. The onset times of patient 1 to patient 5 were