Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
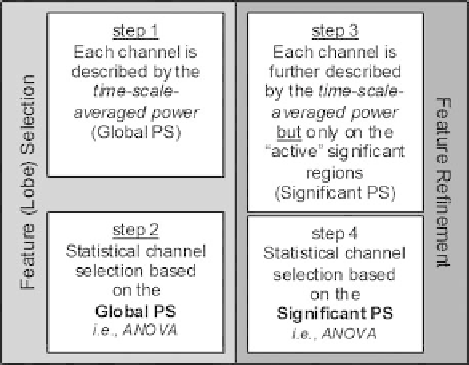
Fig. 3.2: The diagram of the proposed algorithmic transitions, heading toward
derivation of significant activity channels and bands.
of scale
s
is introduced as an alternative to frequency, leading to the so-called time-
scale representation domain.
The CWT of a discrete sequence
x
n
with time spacing
δ
t
and
N
data points (
n
=
0
1) is defined as the convolution of
x
n
with consecutive scaled and translated
versions of the wavelet function
,
N
−
ψ
0
(
η
)
:
n
=
0
x
n
ψ
∗
(
n
−
n
)
δ
t
/
s
,
N
−
1
W
n
(
s
)=
(3.1)
2
1
/
4
e
i
ω
0
η
e
−
η
/
2
ψ
0
(
η
)=
π
,
(3.2)
where
η
and
ω
0
=
6 indicate nondimensional “time” and frequency parameters,
ψ
∗
(
·
)
respectively and
denotes the complex conjugate operation. In our application,
ψ
describes the most commonly used wavelet type for spectral analyses, i.e.,
the
normalized complex Morlet wavelet
given in (3.2). The wavelet function
(
η
)
0
ψ
0
is
a normalized version of
that has unit energy at each scale, so that each scale is
directly comparable to each other. The normalization is given as
ψ
s
0
s
n
−
1
/
2
n
−
ψ
(
n
)
δ
t
/
=(
δ
t
/
s
)
ψ
(
n
)
δ
t
/
.
(3.3)
In principle, a complex wavelet function is better suited for capturing oscillatory
behavior than a real one, because it captures both the amplitude and the phase of
EEG signal. The scale set is given by
s
0
2
j
δ
j
s
j
=
,
j
=
0
, ··· ,
J
,
(3.4)