Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
sidering the effect of error, entities will choose the optimal route with the shortest
processing time if they want to maximize the reward of performance.
Consequently, to model learning, it is first necessary to quantify the learning
process in individual servers. Based on that, the condition under which an entity
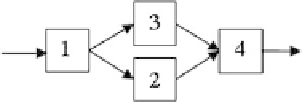
switches between the two routes shown in Fig. 9.6 can be established and proved by
integrating queuing network with reinforcement learning. Finally, this quantitative
condition of route switching can be applied to the more complex model of 18 servers
with two routes (see Fig. 9.5) to generate the basic PRP and the reduction of PRP
during the learning process.
Fig. 9.6: The simplest queuing network with two routes.
9.3.1.1 Learning Process in Individual Servers
Based on the functions of the servers in Table 9.1, the two long-term memory servers
(LTDSM and LTPM) play the major roles in learning phonological judgments (task
1) and choice reaction (task 2) [2]. Because the learning effects of long-term mem-
ory are represented as speed of retrieval of production rules and motor programs
from the two long-term memory servers at the Hicog and the BG servers, it is im-
portant to quantify the processing time of the Hicog and the BG servers. In addition,
because the premotor cortex (PM) server is activated in learning visuomotor associ-
ations [32], changes in the processing speed of the PM server is also to be considered
in the learning process of the model.
Because the exponential function fits the learning processes in memory search,
motor learning, visual search, and mathematic operation tasks better than the power
law [18], it was again applied to model the learning process in the individual servers
here
=
+
(
−
α
)
,
1
/
μ
A
i
B
i
Exp
i
N
i
(9.7)
i
i
) is its processing time;
A
i
: the minimal
of processing time of server
i
after intensive practice;
B
i
: the change of expected
value of processing time of server
i
from the beginning to the end of practice;
μ
i
: processing speed of the server
i
;(1
/
μ
α
i
:
learning rate of server
i
;
N
i
: number of customers processed by server
i
.
For the BG server, 1
/
μ
BG
: motor program retrieving time; ABBGB: the minimal
of processing time of BG server after practice (314 ms, [35]);
B
BG
: the change of
expected value of processing time from the beginning to the end of practice (2
×
314
=
628 ms, assumed);
α
BG
: the learning rate of server BG (0.00142, [18]);
N
BG
: