Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
BOLD Responses to Two Visual Stimuli in Human Brain
2.4
2.2
2.0
1.8
1.6
1.4
1.2
1.0
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
Stimulus Interval (ms)
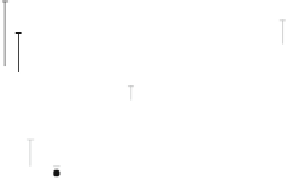
Fig. 11.3. ISI dependent BOLD responses to paired stimulation. Large filled circle indi-
cates that the suppression can vary with stimulation contents.
is incapable of getting activated by a subsequent excitatory input
is detected to be a suppressed state only when the excitatory input
comes. The correlation between fMRI response and visual evoked
potential seen in the human primary visual area with the same
stimulation paradigm also supports that neuronal activity of this
kind of interaction is reflected in fMRI signal
(1)
. The recovery
from the suppressive state in terms of ISI can vary with stimulus
contents as well as the areas that have different functional speci-
ficity as described in the later section
(2,-4)
.
In the following sections, we will show interaction between
functional areas on the dorsal visual pathway with paired “mov-
ing” stimulation and on the ventral visual pathway with paired
“shape” stimulation.
3. Functional
Activation and
Interaction at
Motion
Processing Areas
Evidences from electrophysiology of monkeys and non-invasive
studies of the human brain indicate that visual area MT (or sec-
ondary area V5) is related to the primary motion processing. In
fMRI studies on MT, the activation appeared more clearly when
dots or bars are moved on the screen than when they are standing.
Input characteristics of MT and interaction between functional
units were probed here through an experiment using a paradigm
with paired moving stimulations
(5)
.
In that experiment on MT, we used the following paradigms
I, II and III shown in
Fig. 11.4
. In paradigm, a set of standing
bars was flickered once. In paradigm II, the bars appeared moving
by flickering one bar at a position and then shifted to another
position with a time delay of 50 ms. In paradigm III, the moving
pattern of paradigm II was repeated with 200 ms (50 ms from