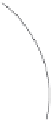Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Electrophysiology
single-and multi-unit activity
local field potential
electroencephalography
magnetoencephalography
Optical imaging
ion flux
blood oxygenation
blood volume
blood flow
MRS
creatine kinase flux (
31
P)
oxygen consumption (
17
O,
13
C)
blood flow (
17
O)
glucose consumption (
19
F)
neurotransmitter flux (
13
C)
MRI
blood oxygenation
blood flow
blood volume
oxygen consumption
water diffusion
neuroelectric effect
cm
2
MRS
mm
0
MRI
Optical imaging
-2
µ
m
Electrophysiology
-4
-4
-2
0
2
4
6
8
ms
s
min
hour
day
Temporal resolution (log seconds)
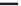
Fig. 1.2. Comparison of spatiotemporal resolutions of current methods used in neuroscience.
this type of cross comparison across methods since then, up-
to-date results were compiled from in vivo dynamic imaging
studies of primarily small animals. Unfortunately, these crite-
ria excluded two dominant techniques in functional brain imag-
ing:
14
C-deoxy-glucose (
14
C-DG) autoradiography and positron
emission tomography (PET).
14
C-DG, a glucose analog, measures glucose consumption
by the amount of metabolically trapped
14
C-DG-6-phosphate
throughout the brain
(64)
. However, about an hour is required
for radioactivity to build up in the tissue.
14
C-DG autoradiogra-
phy provides superior spatial resolution (50-100
m) but it is a
terminal experiment and therefore used only in animals.
PET, fashioned after the
14
C-DG method but designed for
application to humans
(65)
, has several methods for functional
imaging. Glucose consumption measurement is analogous to
the
14
C-DG method except that
18
F-fluoro-deoxy-glucose (
18
F-
FDG) is the glucose analog for PET.
15
O-water is used to measure
blood flow. This is done by injecting
15
O-water into the blood
stream and then detecting the rate of appearance of
15
O-water in
the brain tissue. Carbon monoxide with
11
Cor
15
O, which mim-
ics binding of oxygen to hemoglobin in red blood cells, is used
to measure blood volume. The principle is that carbon monoxide
is blood borne and, therefore, the detected radioactivity is only
representative of the vascular compartment. The blood flow and
blood volume methods in combination with inhaled
15
O-oxygen
can be used to measure oxygen consumption by detecting the rate
of metabolized
μ
15
O-water in brain tissue. In all of these studies,