Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Our recent observation on astrocytic Ca
2
+
signaling will here be
discussed in the context of functional brain imaging.
2. Astrocytes Can
Sense and
Modulate
Synaptic Activity
Astrocytes make contact with most synapses in the CNS and
respond to synaptic activity with increases in cytosolic Ca
2
+
ex
vivo
(4, 23)
. Although astrocytes are electrically non-excitable,
they express receptors for most neurotransmitters
(24)
, includ-
ing glutamate
(1)
,GABA
(4)
, norepinephrine
(25)
and acetyl-
choline
(26)
. Retinal Muller cells and astrocytes also respond to
synaptic release of ATP by activation of purinergic receptors
(14)
.
The types of neurotransmitter receptors found on astrocytes in
situ and in vivo are mainly metabotropic receptors, which link to
the second messenger system including, activation of phospholi-
pase C, adenyl cyclase and production of IP3, Ca
2
+
2.1. Astrocytes
Increase Ca
2
+
in
Response to
Receptors Activation
and cAMP
(27, 28)
(
Fig. 5.1
).
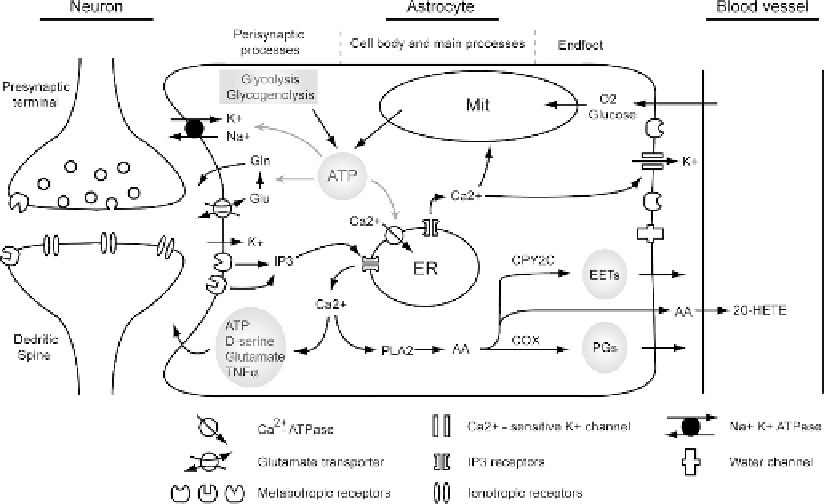
Fig. 5.1. Proposed mechanisms that link synaptic activity, cerebral vasculature regulation and astrocytic energy
metabolism with astrocytic Ca
2
+
signaling. Synaptic released neurotransmitters activate metabotropic receptors in astro-
cytic perisynaptic processes, causing elevation of intracellular Ca
2
+
through a phospholipase C-dependent pathway.
Increases in astrocytic Ca
2
+
are associated with release of gliotransmitters which feed back to the synaptic activity.
Astrocytic Ca
2
+
signaling may also propagate to the astrocytic endfoot, releasing vasoactive agents through phospho-
lipase A2(PLA2)-dependent pathway as well as activation of Ca
2
+
-sensitive K
+
channels. Furthermore, Ca
2
+
is a well
established stimulator of oxidative-phosphorylation which accelerates ATP production from mitochondria (Mit). Due to
the small diameter of perisynaptic processes and the absence of mitochondria in these structures, ATP can also be
generated through glycolysis and glycogenolysis pathways particularly in astrocyte perisynaptic processes. The major
energy consuming processes in astrocyte include converting glutamate (Glu) to glutamine (Gln) after taken up by glu-
tamate transporters, uptake of K
+
from extracellular space through Na
+
-K
+
ATPase and restoring astrocytic cytosolic
Ca
2
+
concentration by activating both plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Ca
2
+
-ATPase.