Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Intact chain of ponds
Permanent, deep ponds provide
habitat for extended tadpole
development
Extensive semi-aquatic vegetation
cover associated with ponds and
drainage lines
Swampy meadow
provides most
refuge below
ground
Run-off fills ephemeral ponds
and flushes terrestrial eggs or
tadpoles into depressions
SATURATED SOIL
Incised channel
Permanent, deep ponds replaced by
ephemeral, shallow ponds periodically
exposed to high energy flows
Little remaining
semi-aquatic
vegetation
Swampy meadow
no longer provides
moist refuge
Ephemeral ponds and
depressions disconnected
from flow of water
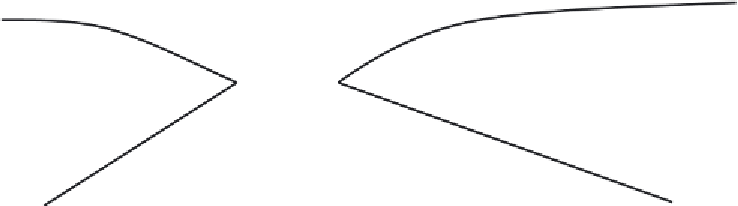
Figure 6.5:
Changes in a stream environment comprised a chain-of-ponds to an incised stream bed resulting
from vegetation clearing and poorly managed streams.
Attributes of well-managed farm dams
Farm dams are bodies of still water. Water will often flow into them, but not from
them, except during floods. Many people do not associate farm dams with native
wildlife, but they can be important environments for frogs and birds. For example,
bird species richness is higher on farms with dams than those where they are
absent. Even the flat muddy areas around farm dams are important environments