Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
4
3.5
3
2.5
2
2.5
2
1.5
70
75
1
80
85
Conversational
symmetry
90
95
100
Conversational efficiency
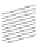
Figure 2.7
The points on each operating curve are a function of the MED imposed. Each plane represents
some network and conversational conditions.
For a two-party conversation, we use the following triplet in 3-D space to
denote the operating point under a given codec and some network and con-
versational conditions:
CQ
2-party
= {LOSQ(MED,
R
),
CE
(MED),
CS
(MED)},
where each axis represents an objective metric measured over a past window,
and
R
is the redundancy degree. Figure 2.7 depicts the trade-offs as a func-
tion of MED and
R
for two conversations of different HRDs and switching
frequencies [4]. For a conversation under some given conditions, the trade-
offs between
CE
and
CS
are shown as a plane parallel to the LOSQ axis.
Under these conditions, the possible LOSQs as a function of MED are shown
by an operating curve on this plane.
The trade-offs shown by each operating curve are very complex and can-
not be represented in closed forms because they involve some network and
conversational conditions that cannot be modeled. Finding the
most probable
operating point on each curve with the best subjective quality (by selecting a
proper MED) proves to be difficult because there are infinitely many operat-
ing points and each involves subjective tests. Also, the operating points do
not have a total order because it may not always be possible to compare two
conversations, one with high LOSQ but low
CS
and another with high
CS
but
low LOSQ. To this end, we use JND as a vehicle to prune operating points
with slightly different conditions that cannot be distinguished.
We have developed a method that uses the JND framework to discretize an
operating curve in Figure 2.7 into a finite and manageable set [4]. Figure 2.8
illustrates the pruning of points on an operating curve that do not need to be
compared against point A. Using subjective tests based on comparison MOS,
which gives a relative subjective comparison of two conversations (similar to
the Comparison Category Rating−CCR−method in ITU P.800 Annex E [12]),