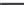
Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Network-control layer
Overlay
network
design
Real-time
network
protocols
Admissions
control
Network topology and protocol parameters
Packet-stream layer
Loss
Concealment
(LC)
Playout
Scheduling
(POS)
Mutual-
Silence (MS)
Equalization
LC and POS parameters
Signal processing layer
Speech
codec
Cross-layer
control
Listening-Only Speech Quality (LOSQ),
Mouth-to-Ear Delay (MED)
Conversational quality control
Subjective/
objective
evaluations
Conversational
conditions
Classifier
design
Figure 2.1
Layers in the architecture of a VoIP system.
talking, and difficulty in conversing during turn taking. Hence, we evaluate
the quality of a conversation over a network connection by the quality of
the one-way speech segments received (the listening-only speech quality or
LOSQ) and that of the interactions [4]; the latter is measured by the delay
incurred from the mouth of the speaker to the ear of the listener (the mouth-
to-ear delay or MED) [6].
When a connection has delays, the MSs perceived by a participant consist
of alternating short and long silence periods between turns [4]. This asym-
metry is caused by the fact that after A speaks, the MS experienced by A (
MS
A
in Figure 2.2) consists of the time for A's (MED
A,B
), the time for B to construct
a response (human response delay or HRD
B
)), and the time for B's response
to travel to A (MEB
B,A
). In contrast, after B hear the speech from A, the MS