Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
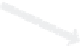
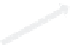
(a) Loop duplication
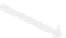
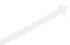
(b) Convergence duplication
Figure 14.15
Packet dropping schemes for two packet duplication problems.
is limited to a small scope. The other two packet dropping schemes are
used to drop duplicate reply packets. The two schemes are the loop
dropping scheme and the convergence dropping scheme. The loop
dropping scheme is used to drop the duplicate route reply packet caused
by loops in a road graph (see Figure 14.15a). The convergence dropping
scheme is used to drop the duplicate route reply packet that is sent from
different directions (see Figure 14.15b).
14.4 Comparison and Discussions
In this section, we compare V2R-based and V2V-based vehicle navigation
systems from the following perspectives: network architecture, comm-
unication mode, and computing mode. Table 14.2 lists the summary of the
comparison results.
From the point of view of network architecture, V2R-based systems
are more complex and more expensive than V2V-based systems. A V2R-
based system requires an infrastructure, which comprises a large number
of roadside units (or sensors), BSs, and TIC. The communication between
vehicles and roadside sensors usually employ VANET. The communication
between BSs and TIC usually employ existing wired or wireless networks,
such as GPRS/3G, WiMax, or frame relay. The total cost for deploying
such an infrastructure is very high. Also, the total cost for maintaining the
infrastructure is high. In contrast, for the V2V-based systems, there is no
need to install and maintain an infrastructure.
From the point of view of the communication mode, V2R-based systems
make use of V2R communication links of VANET to collect real-time traffic
information. Since all roadside units (sensors) are fixed and all V2R links
use one-hop communication, V2R links are quite stable. On the other hand,
V2V-based vehicle navigation systems make use of V2V communication