Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
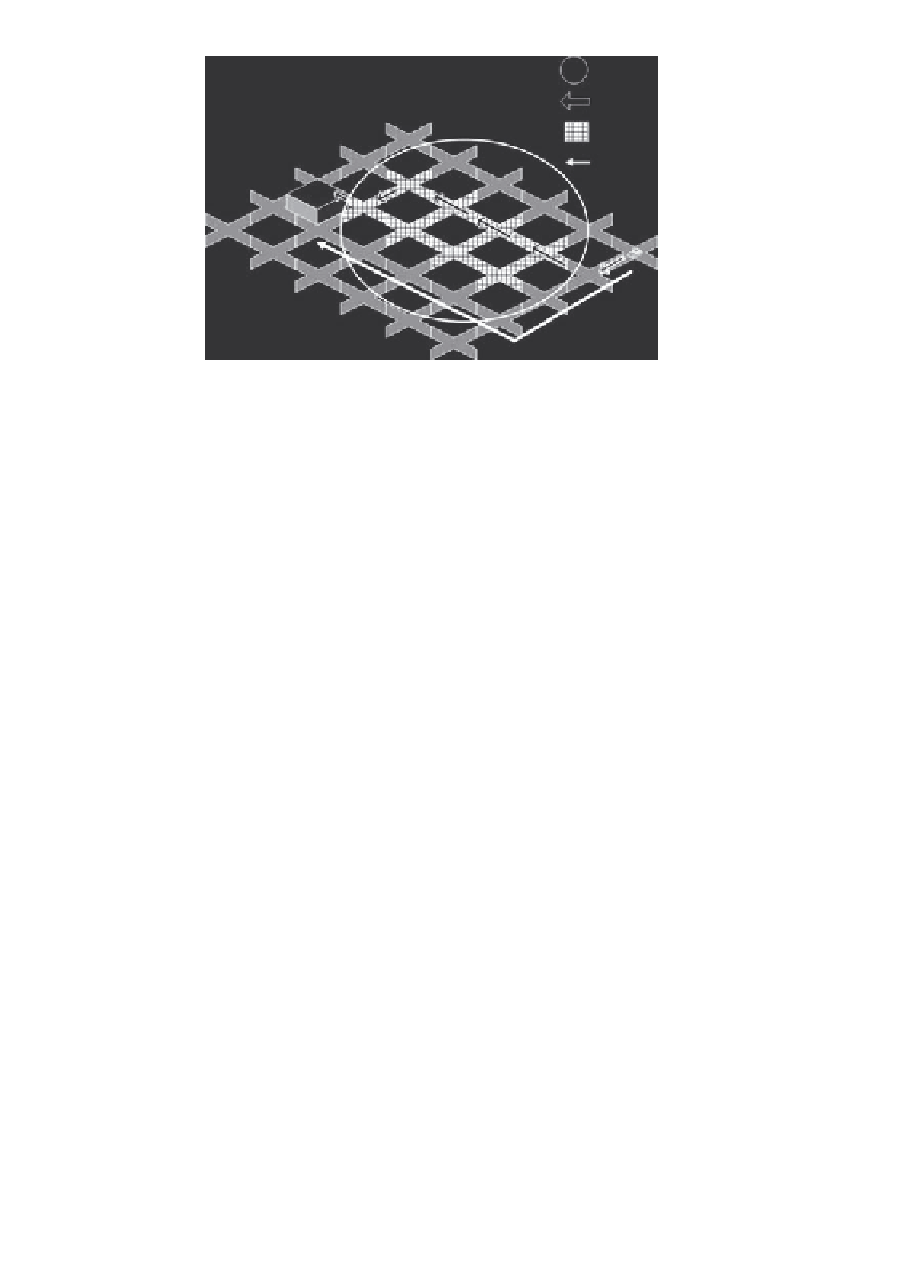
Gathering area
Shortest path
Congestion area
Quickest path
Destination
Figure 14.14
Overview of V2V-based vehicle navigation.
route reply packet, the route reply packet will record the traffic conditions
of all traversed routes. After the guided vehicle receives multiple copies of
the route reply packet from different directions, it can easily calculate the
quickest path according to the real-time traffic information recorded in the
route reply packets. Figure 14.14 shows the shortest packet taken by route
query packet, and the flooding area traversed by the route reply packet, and
then found the quickest route from origin to destination. Note that both
route query packet and route reply packet are relayed by cell heads on a cell-
to-cell basis.
The main problem with the route reply packet is that a simple
unconstrained flooding scheme, unfortunately, will result in a broadcast
storm in VANET. To solve this problem, three packet dropping
mechanisms are developed [2] to limit the scope of flooding. The most
important one is the long-route dropping scheme. During the delivery
process of the route query packet, the query packet will record the traffic
conditions of all traversed routes. After the destination cell head receives
the route query packet, it can make use of this traffic information to
estimate the travel time for a vehicle to traverse the shortest path. We
call this time shortest-path travel time. Similarly, during the delivery
process of the route query packet, the query packet will record the traffic
conditions of all traversed routes. Due to flooding, the route reply packet
will discover multiple potential routes for guided vehicles. When an
intermediate vehicle in a potential route receives a route reply packet, it
first estimates the travel time from the destination cell head to itself. If
the estimated travel time has exceeded the shortest-path travel time, it
knows that this potential route is useless since it results in longer travel
time than the shortest path. Therefore, when such an event occurs, the
intermediate vehicle drops the route reply packet and stops the flooding
of the reply packet. It can be seen in Figure 14.14 that the flooding area