Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
V2V-based approach, there is no need for an infrastructure. Each vehicle
that needs navigation collects real-time traffic information by using V2V
communication links, as shown in Figure 14.11. Also, each vehicle that needs
navigation will calculate the quickest route by itself according to the collected
real-time traffic information.
To reduce the large communication overhead incurred by V2V comm-
unication, cell-based data aggregation and packet relay is adopted. That
is, a road segment is divided into several fixed cells, as shown in Figure
14.10. Herein, a road segment is defined as a section of a road between two
intersections. All vehicles within a cell share similar traffic conditions. Each
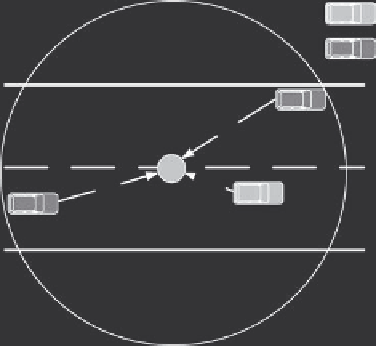
cell has a cell head: a car in a cell that is the closest to the cell center will
be elected as a cell head (see Figure 14.11). A cell head is responsible for
collecting the traffic information of a cell. To do so, all vehicles in a cell
exchange their basic data (such as driving speed and driving direction) by
periodic broadcasting hello messages. Then, a cell head can easily learn of
the traffic condition in a cell, such as the number of cars in a cell and the
average driving speed in a cell. To uniquely identify a cell, in the digital
Cell-1
Cell-2
Cell-3
Cell-4
Cell-5
Figure 14.10
Driving a road segment into cells.
Cell head
Cell member
Figure 14.11
Cell head and cell members.