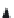Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Possible path
2
1→2→4
1→3→4
1→2→3→4
1→3→2→4
1
4
3
Possible path
1→2→5
1→3→5
1→4→5
1→2→3→5
1→3→2→5
1→3→4→5
1→4→3→5
1→2→3→4→5
1→4→3→2→5
2
3
5
1
4
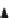
Figure 14.2
Potential routes in road graphs.
In a road graph, there may exist multiple paths between any two given
nodes. As shown in Figure 14.2, the number of possible paths increases rap-
idly with the number of nodes in the graph. Each possible path may be a route
candidate since each possible path may take less travel time than the shortest
path. Therefore, for a large area, it is challenging to find all quicker paths
between any two given nodes according to the real-time traffic information.
14.1.2 Three Types of VaNeT-Based Vehicle Navigation Systems
The VANET-based vehicle navigation systems can be classified into three
types of categories: (1) V2R-based, (2) V2V-Based, and (3) hybrid. Figure 14.3
shows the architecture of a V2R-based vehicle navigation systems. V2R-based
systems adopt a centralized and hierarchical architecture [8,9,10,14]. In this
type of architecture, a large number of roadside units (or wireless sensors)
and base stations (BSs) need to be deployed along the side of all roads. The
roadside units use V2R communication links to communicate with onboard
units of passing vehicles to collect local traffic information, such as the num-
ber of cars on a road and the average driving speed on a road. Then, the BSs
transmit the collected local traffic information to a traffic information center
(TIC). The TIC merges the collected local traffic information to generate a
wide-area traffic information. The advantage of V2R-based architecture is
that V2R links are reliable since roadside units are fixed and V2R links use
one-hop communication. The disadvantage of V2R-based architecture is that
it is very costly since an infrastructure consists of a large number of roadside
units, BSs, and traffic information centers (TICs).
Figure 14.4 shows the architecture of the V2V-based vehicle navigation
systems. V2V-based systems adopt a decentralized and flat architecture