Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
A0000000
90000000
88000000
80000000
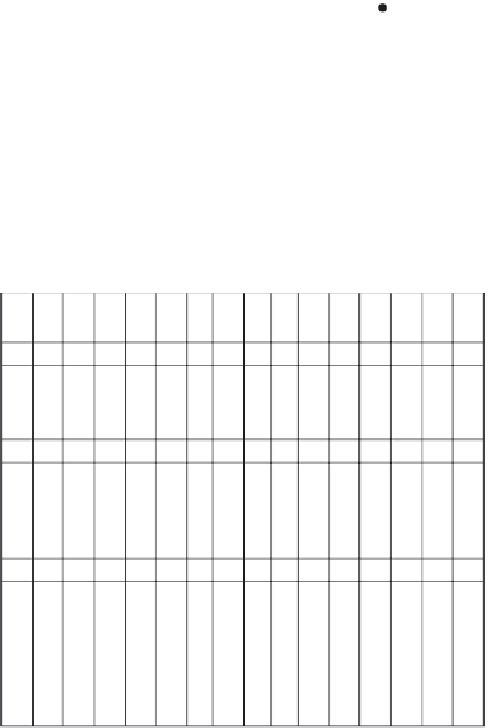
Figure 1.14
A sample nodeId space enlarged from 80000000 to A0000000.
0
12345
7 89abcdef
xxxxxx xxxxxxxxx
66666
6 666666666
01234
6
7
8 9abcdef
xxxxx
x xxxxxxxxx
66666
6
6 666
6 6666
55555
5
5 555
5 5555
01234
5
6
7
8
9
b cdef
xxxxx
x
x xxx
x xxxx
6
666
6
6 666
6
6 6666
5
555
5
5 555
5
5 5555
a
aaa
a
a aaa
a
a aaaa
0
2 34 7
5
6
8 9abcdef
x
xxx
x
x xxx
x
x xxxx
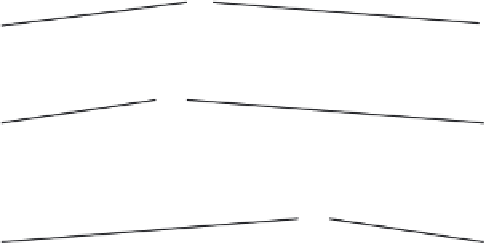
Figure 1.15
Routing table of a Pastry node with nodeId
65a1x
,
b
= 4. Digits are in base 16,
x
represents
an arbitrary suffix. (From Castro, M., Druschel, P., Kermarrec, A.-M., and Rowstron, A.,
Proceedings of SIGOPS European Workshop, France, September 2002. With permission.)
with the nodeId closest to the message key. Figure 1.16 shows the process of
routing a message.
The DHT-based P2P networks have some disadvantages. First, they do not
adapt well to node churns. The overhead of joining and leaving the network
is usually high; therefore, as nodes join and leave the network frequently,
the performance degrades. Second, DHT-based P2P networks do not sup-
port substring search. Due to the nature of the hash function, if there would
be any modification of the message, the key generated by the hash function
will be totally different. Therefore, the user would not be able to just use the
substring of the key to search for a message.