Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
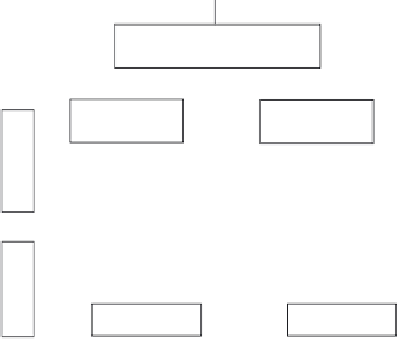
Image similarity
s
Feature aggregation
s
1
s
n
. . .
Feature
similarity
Feature
similarity
. . .
q
1
q
n
X
1
. . .
X
n
Feature
1
Feature
n
. . .
Query image
Figure 11.6
Feature aggregation in content-based image retrieval.
and
i
= (1, … ,
n
) is the
i
ith visual feature. The overall aggregated similarity
of multiple visual features is the ultimate criterion for image ranking; there-
fore, it determines the overall performance of the retrieval. In the literature,
physical similarities in retrieval systems are defined either as a probability
that one image is similar to another or a metric of visual features of images.
It does not matter that the similarity is defined as a probability or a metric; it
must answer the question of how the aggregated similarity of multiple visual
features can be measured and measured consistently as humans do.
Various classifier combination schemes are used that equivalently yield
a dissimilarity function
D
(...). Though combination schemes are evaluated
against their statistical performance, the question remains what combina-
tion scheme would meet the query requirements.
11.3.2 Linear Combination of Visual Features
The intuitive and straightforward solution is to aggregate multiple features
using a linear combination of individual feature distances. To factor the rela-
tive significance of various features, the weighted combination is a popular
suggestion [4,7], as expressed in the following.
L
∑
Dd d
(, ,
…
=
,
d
)
wd
(11.23)
12
L
l
l
l
=
1