Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
MSCM
Request
Response
Command
Indication
. . .
. . .
. . .
and so on
and so on
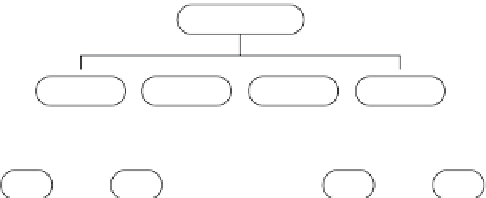
Figure 3.10
Hierarchical representation of the H.245 messages. (From Du, Y., “UBI-Media” Conference of
IEEE, 2008. With permission.)
protocol is responsible for the call setup and conversation continuation, by
efficiently handling of its message exchanges, will eventually lead to shorter
call setup time and better conversation quality. Also in high traffic condi-
tions, for handling large numbers of calls concurrently and to provide good
conversational quality (the QoS), H.245 is the only vital protocol that should
be taken care of properly.
According to the ITU-T X.691 recommendation, H.245 messages are ini-
tially in the form of ASN.1 and then they are converted into binary streams,
when the call is initiated. After a requested terminal receives the bit stream,
it reconstructs those messages back into meaningful ASN.1 text and then it
sends proper responses to react to the requester terminal.
In the H.245 module, messages are defined in a tree-like structure as
is depicted in Figure 3.10. This defines a general message type called,
MultimediaSystemControlMessage (MSCM). MSCM further comprises four
different types of special messages, namely, request, response, command,
and indication. A request message corresponds to a specific action and
requires an immediate response through a response message. A command
message requires an action but no explicit response. An indication message
contains information that does not require action or response.
A response message requires specific action and an immediate response.
A command message requires an action but no explicit response. An indica-
tion message contains information that does not require action or response.
3.4.2.1 Characteristics of H.245 Messages in 3G System
The most common H.245 messages for a 3G video call are
1. TerminalCapabilitySet
2. TerminalCapabilitySetAck
3. MasterSlaveDetermination