Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
B
A
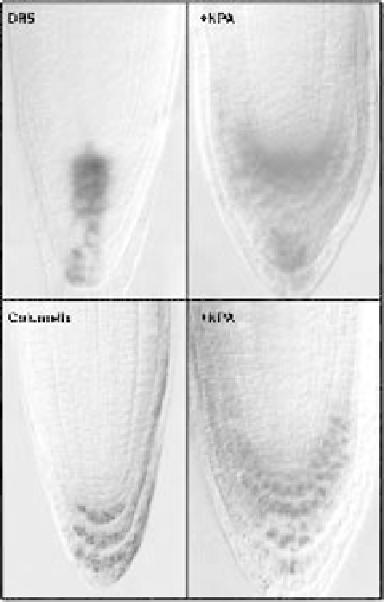
Figure 8.3
The auxin response element promoter DR5, fused with the GUS gene marks the auxin
maximum in the distal most cells of the root tip. (A) GUS expression is severely changed after treatment
with polar auxin transport inhibitor naphtylphtalamic acid (NPA). NPA treatment also alters the size
and shape of the columella root cap domain, indicated here by staining of the starch granules. (B) Stem
cell maintenance model. The cells that surround the QC are kept in an undifferentiated state by
short-range signals that suppress progression of cell differentiation. Adapted from Scheres
et al.
(2002).
The octant stage (when the hypophysis cell is formed) is the first time when the
apical-basal polarity can be observed. In
gnom
mutants the hypophysis cell does
not develop and in severe mutants the apical-basal polarity is completely missing
(Mayer
et al.
, 1991, 1993).
GNOM
encodes a brefeldin A (BFA)-sensitive ARF
GDP/GTP exchange factor that is required for the proper polar localization of auxin
transporter PIN1. Treatment of embryos with BFA resulted in mislocalization of
PIN1 (Geldner
et al.
, 2001), which could be avoided with engineered BFA-resistant
GNOM (Geldner
et al.
, 2003). This supports the idea of polar auxin transport being
the mediator in establishing apical-basal polarity.
The embryo starts its own auxin production most likely at the globular stage,
which was shown by the accumulation of auxin when embryos at this stage were
treated with NPA or in
gnom
mutants. During this stage, PIN1 is polar localized to
the basal membranes of the provascular cells while PIN7 localization is reversed,