Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
3.5.2.2 Enterprise Grid
The term Enterprise Grid is used to refer to application of Grid Computing for
sharing resources within the bounds of a single company (Goyal and Lawande 2005).
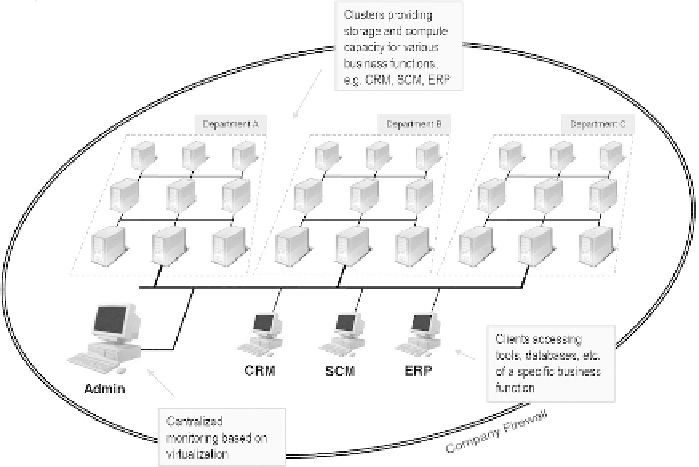
All components of an Enterprise Grid operate inside the firewall of a company, but
may be heterogeneous and physically distributed across multiple company locations
or sites and may belong to different administrative domains (see fig. 3.3).
Fig. 3.3:
Example Enterprise Grid infrastructure
With specific Enterprise Grid middleware, the available IT resources are virtualized
and can be managed in a unified and central way. They can also be allocated to proc-
esses according to demand.
According to NESSI-Grid (2006), commercially available solutions for
Enterprise Grids feature policy-based scheduling of workload management on
heterogeneous infrastructures made out of desktops, servers and clusters. These
systems contain basic resource control and mechanisms for fault tolerance as well
as analysis tools for performance and debugging. Due to the lack of standardization
in this space, these solutions typically support a variety of de facto standards and
translate them into a solution specific format. Finally, these solutions often contain
their own billing and user management solutions, partially integrating with common
security infrastructures prevalent in enterprises.
Example
One example of Enterprise Grids is the Grid of the pharmaceutical company
Novartis. Novartis started a five-year initiative for creating an Enterprise Grid in
2003 in order to support compute- and data-intensive research tasks, as for example