Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
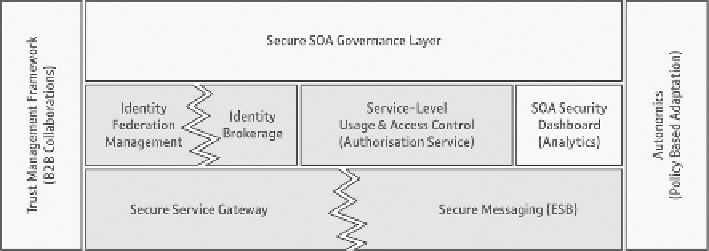
(Dimitrakos et al. 2009b). In this section we focus only on two representative exam-
ples of the security capabilities: federated identity brokerage and distributed access
management. For a full description of the security capabilities shown in figure 8.2,
please refer to Dimitrakos et al. (2009a) and Gridipedia (2009b).
Fig. 8.2:
Overview of the security capabilities required by service-oriented enterprises
These security capabilities have been validated by the Business Experiment
BEinEIMRT (see chapter 9) demonstrating the secure integration of an in-cloud
High Performance Computing (HPC) capability into a regional NHS network in
Spain in order to facilitate the fast processing of radiotherapy analysis results while
preserving patient privacy and ensuring the correct association between patients and
their radiotherapy examination data. Most of these capabilities together with rele-
vant capabilities from VO Management have also been validated in a BE demon-
strating a network-centric distributed platform for scalable, collaborative online
gaming (see chapter 12).
8.3.1 Federated Identity Management
8.3.1.1 Identity Brokerage and Identity Federation Context Management
This is a capability enabling identity federation and brokerage across business part-
ners. Early developments of this capability stemmed from collaborative research
between BT and the European Microsoft Innovation Centre in the TrustCoM project
(Dimitrakos et al. 2004). It is a customizable platform for Identity-as-a-Service
(IDaaS) provision with technological innovations that resulted in the following
differentiators compared to what is currently available in the market:
• The business logic of the Identitty Broker can be optimized for each identity
federation context. This innovation enables the application of different authen-
tication procedures, different federated identity standards, attribute types and
entitlements on the same user or resource depending on the purpose of a B2B
interaction and the scope of the identity federation. The Identity Broker is
therefore configured to compose security primitives in a behaviourally distinct
instance of a Security Token Service (STS) optimized for the specific context.