Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
and Crisp z
i
and Crisp z
i
(a) Crisp Υ
T
(b) Fuzzy Υ
T
and Fuzzy z
i
and Fuzzy z
i
(c) Crisp Υ
T
(d) Fuzzy Υ
T
(e) Crisp Υ
T
and
(f) Fuzzy Υ
T
and
S
ω
: G×G→{0, 1}
S
ω
: G×G→{0, 1}
(g) Crisp Υ
T
and
(h) Fuzzy Υ
T
and
S
ω
:
G
×
G
→[0
,
1]
S
ω
:
G
×
G
→[0
,
1]
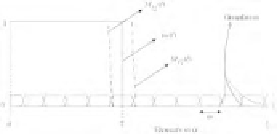
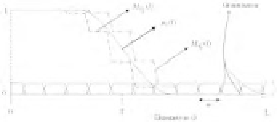
FIGURE 3.4: The different forms that the lower and upper approximation of Υ
T
can take when
used to get the grayness ambiguity measure
The grayness ambiguity measure Λ of I is obtained as a function of T , which characterizes
the underlying set Υ
T
, as follows
%
ω
(Υ
T
) log
β
%
ω
(Υ
T
)
β
+ %
ω
(Υ
T
) log
β
%
ω
(Υ
T
)
β
Λ
ω
(T ) =−
1
2
(3.30)
Note that, the above expression is obtained by using %
ω
(Υ
T
) and %
ω
(Υ
T
) in the proposed
logarithmic (L) class of entropy functions given in (3.8), instead of roughness measures.
When the proposed exponential (E) class of entropy functions is used, we get
%
ω
(Υ
T
)β
1−%
ω
(Υ
T
)
+ %
ω
(Υ
T
)β
1−%
ω
(Υ
T
)
1
2
{
Λ
ω
(T ) =
(3.31)
It should be noted that the values %
ω
(Υ
T
) and %
ω
(Υ
T
) in (3.29) are obtained by considering
'weighted cardinality' measures instead of cardinality measures, which are used for calcu-










Search WWH ::

Custom Search