Database Reference
In-Depth Information
A brief introduction to a data model
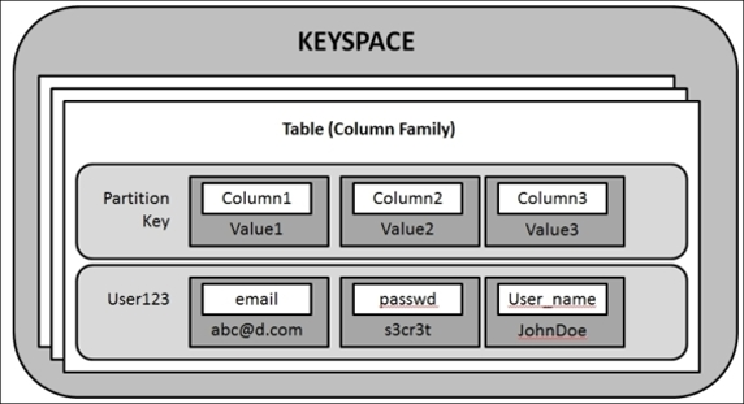
Cassandra has three containers, one within another. The outermost container is
keyspace
.
You can think of keyspace as a database in the RDBMS land. Tables reside under keyspace.
A table can be assumed as a relational database table, except it is more flexible. A table is
basically a sorted map of sorted maps (refer to the following figure). Each table must have
a primary key. This primary key is called
row key
or
partition key
. (We will later see that
in a CQL table, the row key is the same as the primary key. If the primary key is made up
of more than one column, the first component of this composite key is equivalent to the
row key). Each partition is associated with a set of cells. Each cell has a name and a value.
These cells may be thought of as columns in the traditional database system. The CQL en-
gine interprets a group of cells with the same cell name prefix as a row. The following fig-
ure shows the Cassandra data model:
Note that if you come with Cassandra Thrift experience, it might be hard to view how Cas-
sandra 1.2 and newer versions have changed terminology. Before CQL, the tables were
called
column families
. A column family holds a group of rows, and rows are a sorted set
of columns.