Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
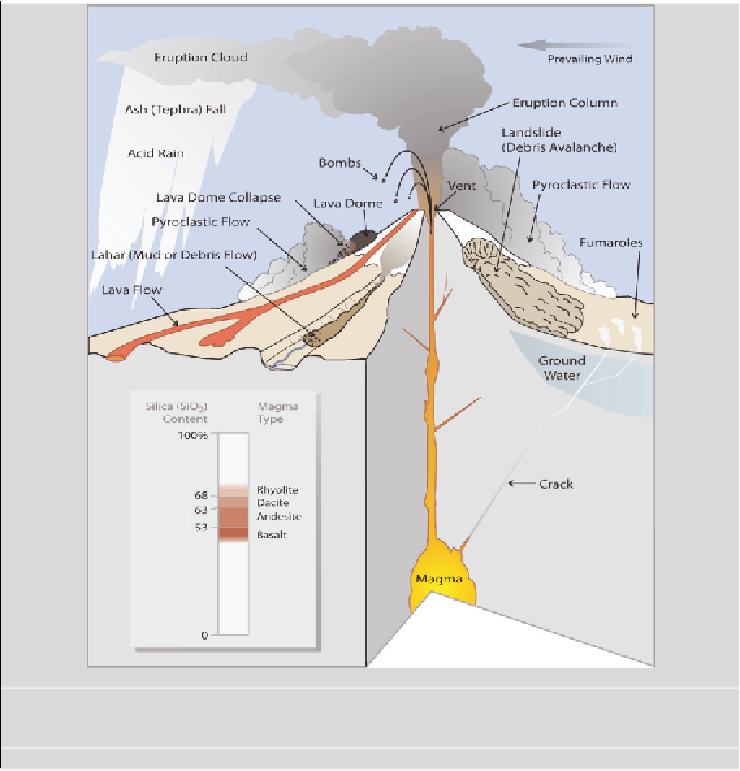
Figure B2.5
Some of the phenomena at volcanoes that transport mass and energy to the
surface and create volcanic hazards. Modern volcanology seeks a quantitative understanding
of these processes and their interactions. SOURCE: Myers et al. (2008).
INTERACTIONS AMONG CLIMATE, SURFACE PROCESSES,
TECTONICS, AND DEEP EARTH PROCESSES
One of the major advances in the Earth sciences over the past decade was the
recognition and verification of broad connections between climate, surface processes,
and tectonics. The NRC
Landscapes on the Edge
(2010a) report identified research
questions that center on interactions among climate, topography, hydrology and
hydrogeology, physical and chemical denudation, sedimentary deposition, and rock
deformation in tectonically active mountain belts as particularly intriguing. While the
feedbacks between tectonics, climate, erosion, and deposition have been the focus of
field studies and numerical simulations over the past decade, elucidating connections
between these processes continues to drive discoveries. Such feedbacks influence the



Search WWH ::

Custom Search