Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
the inclusions and the zircons themselves suggest crystallization in an unusually cool
geothermal gradient. These observations evoke an environment remarkably similar to the
conditions under which modern granites form in subduction environments. Thus, it has been
argued that within just a few hundred million years of the formation of the planet, a stable
siliceous crust, an active hydrosphere, and a form of plate tectonics with marked similarities
to the current regime had already been established.
Further advances in this field may come from identification of new localities where
extremely old rocks and detrital minerals occur. This task will require application of a variety
of geochemical and petrological methods, especially in geochronology. The magnitude of the
undertaking is illustrated by the work invested to identify the oldest zircons from the Jack
Hills. Ion microprobe analyses of more than 100,000 individual zircons were required to
identify the ~100 crystals with ages >4.2 Gyr (Holden et al., 2009).
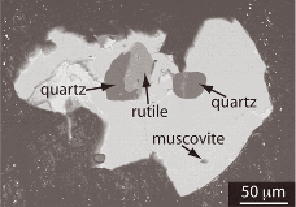
Figure B2.2
Jack Hills: a 4.06-billion-year-old Jack Hills zircon with mineral inclusions that
characterize the parent magma's protolith and melting/crystallization conditions. SOURCE:
Hopkins et al. (2008). Reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd.
The Hadean Mantle and Core
Most of the major questions posed for the early surface environment also
involve the composition and dynamics of the Hadean mantle, and some of these also
involve the early state of the core. For example, the thermal and compositional
stratification of the mantle following the major phase of core segregation (and magma
ocean solidification) constitute the “initial conditions” for subsolidus mantle
convection. In the same way, conditions in the core inevitably changed once the
major differentiation had occurred. Evidence for these transitions can be found in the
context of the search for ancient rocks and minerals described previously.
Geobarometry and geothermometry techniques can infer mantle temperatures and
pressures, and magnetized samples provide information about the nature of the early
geodynamo and also on the energetics of the Hadean deep Earth.
An Early Earth Initiative
This suite of topics involving the early Earth emerges as a major research
opportunity because there have been significant advances in theory, observations, and
modeling capabilities across all of the related areas but little coordination of the
research agenda. Developing a community focus on these topics and coordination of




Search WWH ::

Custom Search