Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Data Protection Manager (DPM) is the data protection, or backup and recovery element, of
the System Center suite. Even though you are likely to deploy your private cloud workloads
on to a fabric of highly redundant storage, network, and compute resources, hardware redun-
dancy doesn't obviate the need for data protection. This is because you can lose critical data
to other events like software errors, malware, or end users simply making mistakes.
DPM storage pools
A DPM storage pool is a collection of disks that DPM uses to store backup replicas and re-
covery points for the workloads that it protects. While DPM can also write data to tables, and
store data in a Microsoft Azure recovery vault, the primary location for DPM to store pro-
tected data is within a storage pool.
DPM storage pools have the following requirements:
■
DPM storage pools must be located on disks separate to the ones that host the system
files, database files, and program files.
■
A storage pool must exist before DPM can start protecting data.
■
A storage pool can contain a single disk. You can add more disks to a storage pool at a
later point in time.
■
DPM storage pools do not support USB/1394 disks.
■
DPM storage pools can only allocate space that exists in volumes it creates on disks.
DPM ignores any existing volumes on a disk added to a storage pool.
■
To maximize the amount of space allocated on a disk that you are going to add to a
storage pool, delete any existing volumes prior to adding the disk to the pool.
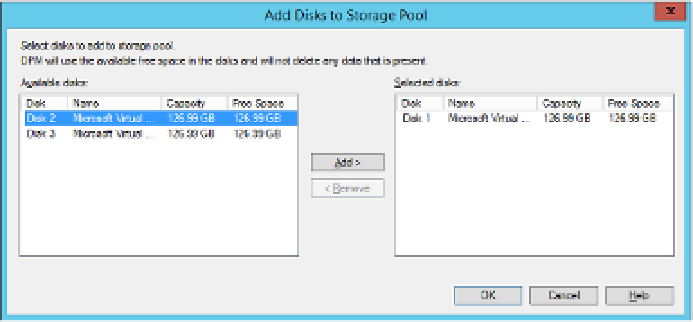
To add disks to a DPM storage pool, perform the following steps:
1.
In the Management workspace of the DPM console, click Disks, and then on the rib-
bon, click Add.
In the Add Disks To Storage Pool dialog box, shown in Figure 2-1, select the disks that
you want to add, and click Add.
2.
FIGURE 2-1
Adding disks to storage pool