Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
ground surface
grate inlet
inflow
catch basin
hood
floatables
outflow
stored water
debris
drain
(a)
(b)
Figure 6.14.
Catch basin and drainage system connection. (a) Schematic diagram; (b) installed catch basin with associated piping.
the hood, and also shows that inlets from multiple
drains can enter the catch basin. To maintain the
effectiveness of catch basins for pollutant removal,
they must be cleaned about twice a year, depend-
ing on local conditions.
6.2.3.5 Detention-Retention Facilities.
Ponds and
storage basins are the most common practices in urban
stormwater management. The combination of a pond
(storage and treatment), wetland (treatment), and infil-
tration or irrigation infrastructure can result in zero-
discharge sustainable stormwater disposal and reuse.
The sizing of storage basins can best be accomplished
by continuous simulation models, since it requires con-
sideration of storage changes resulting from transient
inflow and the rate at which the storage basin is emptied
after a storm. The key design parameter is usually the
total volume captured, which is called the
water-quality
volume
. The two types of detention basins used for
quality control of urban runoff are wet detention ponds
and extended or modified dry ponds.
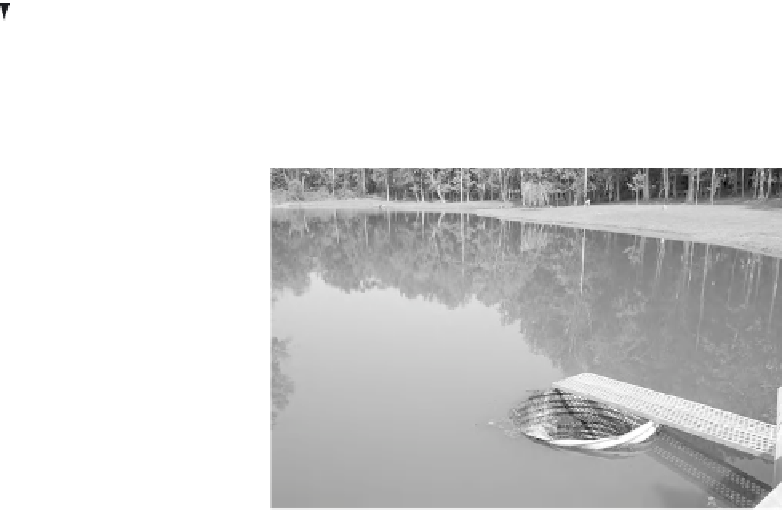
Figure 6.15.
Wet detention pond.
maintenance can make such facilities an eyesore
and a mosquito-breeding mudhole. A typical well-
designed wet detention pond consists of (1) a
permanent water pool, (2) an overlying zone in
which the design runoff volume temporarily
increases the depth of the pool while it is stored
and released at the allowable peak discharge rate,
and (3) a shallow littoral zone that acts as a
biological filter. The depth of wet detention ponds
should be in the range of 1-3 m (3-10 ft), and it
is important that the side slope of the pond be
less than 5:1 (h :V) to minimize the danger of
drowning. The effectiveness of wet detention
ponds in removing contaminants can vary signifi-
cantly between contaminants, and the removal
Wet Detention Pond.
A
wet detention pond
has a per-
manent pool of water, and a simple wet pond acts
as a settling basin with relatively low efficiency.
A typical wet detention pond with the outlet struc-
ture in the foreground is shown in Figure 6.15,
where the outlet structure consists simply of a cor-
rugated metal riser (i.e., a corrugated metal pipe).
Accumulated solids must be removed (dredged)
to maintain the removal efficiency and the
aesthetics of the pond. Improper design and


















Search WWH ::

Custom Search