Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
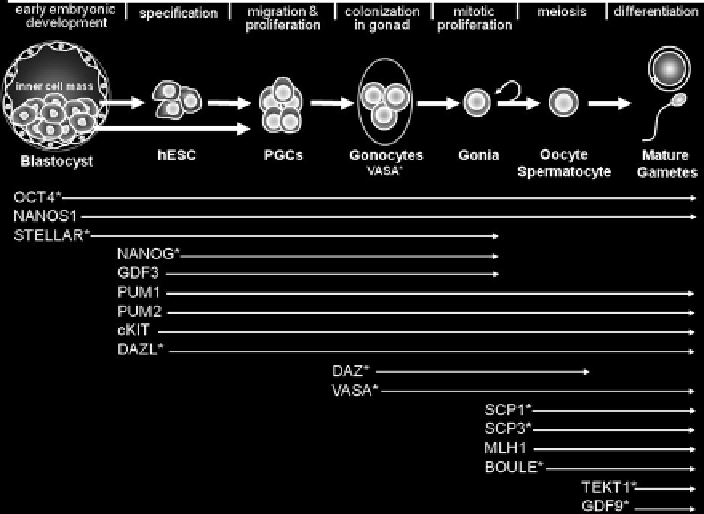
Fig. 3.4
Diagrammatic representation of the different stages of human germ cell development
during human ES cell differentiation resolved from both
in vivo
and
in vitro
studies. Shown are
the expression patterns of genes that define undifferentiated ES cells and each subsequent stage of
germ cell development with each gene name on the left and its temporal expression indicated by
the
arrows
extending to the
right
. All of the genes are enriched in germ cells relative to somatic
cells, and those that are only expressed in the germ cells following the blastocyst stage embryo
in vivo
are indicated by an
asterisk
. Note that
Gdf9
is an adult oocyte-specific marker in mouse,
and
TEKT1
is an adult spermatid-specific marker in human and mouse
those that were germ cell-specific (not expressed in somatic lineages), and those
that were germ cell-enriched (highly expressed in germ cells with limited expres-
sion in somatic cells). The genes
GDF3
and
NANOG
were expressed in undifferen-
tiated ES cells. Surprisingly however, as depicted in Fig.
3.4
, undifferentiated
human ES cell colonies also expressed RNA and protein for the germ cell-specific
genes
DAZL
and
STELLAR
, as well as the germ cell-enriched genes
cKIT
(a marker
of premeiotic migrating germ cells and pre-meiotic germ cells of the postnatal
testis), and
NANOS1
,
PUM1
, and
PUM2
(markers specific to premeiotic primordial
germ cells of the fetal gonads) (Clark et al.
2004a
).
The presence of this early germ cell program in undifferentiated hESCs indi-
cates that either: hESCs originate from PGC precursors in the inner cell mass;
hESCs and PGCs share common genetic programs of pluripotency, self-renewal,
and survival; and/or that a subpopulation of hESCs spontaneously differentiates
into the germ cell lineage. In support of the hypothesis that hESCs
in vitro
and the
inner cell mass
in vivo
are not identical cell populations it was discovered that the
transcriptional profiles of these cell types were different. Cells of the inner cell
Search WWH ::

Custom Search