Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
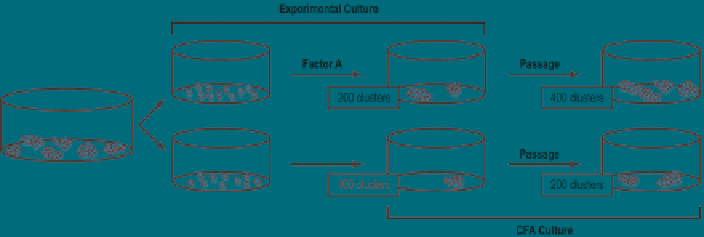
Fig. 6.2
A schematic representation of a hypothetical experiment to analyze the effect of Factor
A on SSCs
in vitro
. Established clusters (the far left well), cultured under standard conditions, are
digested and plated in two groups of culture. In one, target cells are initially incubated with Factor
A for 6 days, producing 200 clusters (experimental culture). These clusters are digested into single
cells, replated on a feeder layer, and cultured for an additional 6-day period under the standard
cluster-inducing condition without Factor A (CFA culture), generating 400 clusters. In the other
group (control), target cells are cultured similarly to the factor-treated group for two culture
cycles, but Factor A is not used in the experimental culture. Under this condition, 100 and 200
clusters are derived in the experimental and CFA cultures, respectively. See text for discussion on
the data interpretation
These results indicate that twofold more SSCs, which were placed in culture on
day 0, survived for 6 days and formed clusters in the presence of Factor A, com-
pared to the control culture. Therefore, an experimental culture generates informa-
tion about maintenance or survival of SSCs and their cluster-forming capacity.
However, it is of note that the twofold increase in cluster numbers cannot necessar-
ily be attributed to SSC proliferation, because SSCs proliferate within a cluster.
In order to unmask SSC proliferation taking place inside clusters, they need to be
digested so that SSCs are released from the cluster structure, and replated into a second-
ary culture: i.e., the CFA assay (Fig.
6.2
). These secondary clusters are induced using
the identical, standard condition in both groups (in this case, without Factor A). Thus,
the degree of SSC proliferation
in each group
can be measured by the differential in
cluster numbers between the experimental and CFA cultures (Fig.
6.2
). As explained
below, by comparing two values of the differential, derived in the factor-treated and
control groups, the effect of Factor A on SSC proliferation can be revealed.
In this hypothetical experiment (Fig.
6.2
), 400 clusters were found in the CFA
culture in the factor-treated group and 200 clusters in the control group. This indi-
cates that SSCs proliferated twofold in “both” groups: 200-400 in the factor-treated
group and 100-200 in the control group. Together with the cluster counts in the
experimental culture, therefore, the data indicate that Factor A did not stimulate
SSC proliferation, but likely promoted SSC survival.
As such, SSC survival and proliferation can be distinguished more readily with
the CFA assay than with the transplantation assay. To measure the degree of SSC
proliferation with the transplantation assay, transplantation needs to be done at both
the beginning and end of the experimental culture; thus, the CFA culture is equiva-
lent to transplantation after the experimental culture.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search