Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
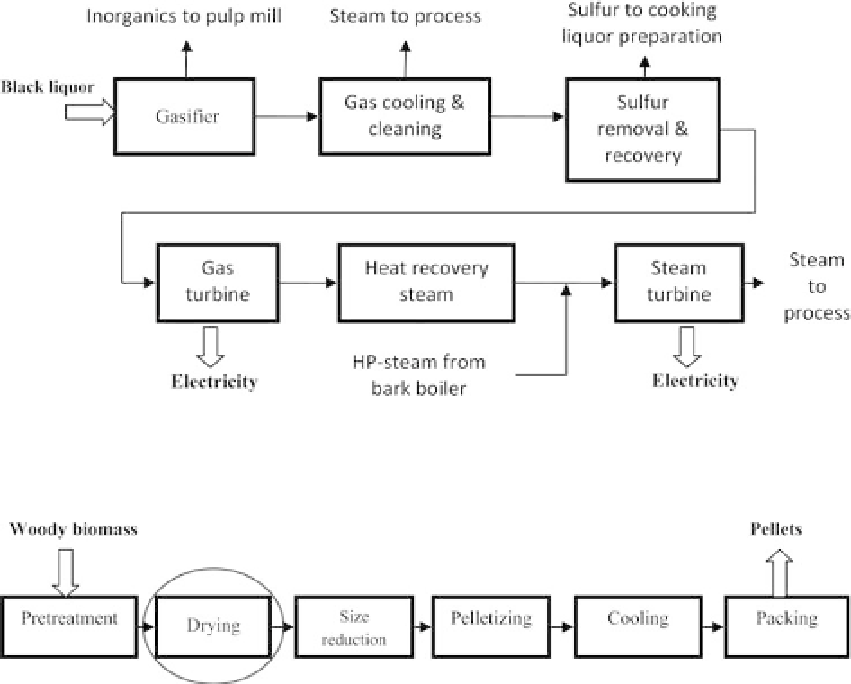
Figure 10.4. Potential electricity generation using black liquor gasification combined cycle (BLGCC)
(Source: Naqvi
et al
., 2010b).
Figure 10.5. Simplified flow diagram of pellet production process.
heat from the pulp industry could be used for integrated pellet production that requires drying of
the biomass. From the results of the Ecocyclic Pulp Mill (KAM) report, the chemical pulp mills
have surplus of biomass in the form of bark i.e. about 70,700 tonnes of bark per year (KAM,
2003). It is worthwhile for the pulp mills to produce pellets due to continuous increasing demand
for biofuel in the heating sector. The major steps in the pellet production process are discussed
and is shown in Figure 10.5 (Zakrisson, 2002).
1. Pretreatment: the biomass is chopped and metals are removed.
2. Drying: the dry solid contents in the biomass are increased from 45% to 89%.
3. Size reduction: the size of particles is reduced using a hammer mill.
4. Pelletizing: the pellet press is used to press wood particles to shape pellets.
5. Cooling: the pellets are cooled using air.
6. Packing: the pellets are sacked or transport to storage facility.
The most important process step in pellet production is drying of the biomass, which requires
most of the heat energy. A brief description of dryers that could be considered in the integrated
pellet production and pulp mill is presented:
•
Steam dryer
: the medium pressure steam can be used to dry the biomass and the heat from
removed moisture can be recovered as low-pressure steam. The steam drying technology is
efficient but the steam obtained is relatively at low pressure and temperature in comparison
with the steam fed.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search