Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
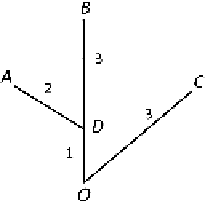
We illustrate the EBD distribution with an example. In Fig.
2.1
nodes are labelled
by letters and arc lengths indicated by numbers. To calculate the EBD distribution
on this network, first note that there are two branches at
O
, which must have equal
search density. This can be achieved by assigning hider probability 3
3to
the branch consisting of the arc
OC
, and probability 2/3 to the other branch. The
branch node
D
has two branches, and to ensure these have equal search density, the
hider probability assigned to the arcs
AD
and
BD
must be proportional to 2 and 3,
respectively. Hence the probabilities the hider is at nodes
A
and
B
are 2
/
9
=
1
/
/
·
/
=
5
1
3
/
/
·
/
=
/
/
2
15 and 3
5
1
3
3
15 respectively. The probability the hider is at
C
is 1
3.
Fig. 2.1
A tree network
In [
10
], Gal shows that if the hider uses the EBD distribution, this ensures that
any depth-first search of
Q
, and in particular any CPT finds the hider in expected
time exactly
¯
2, which must therefore be the value of the game. In the case of
the network in Fig.
2.1
, the value of the game is
μ
=
μ
/
μ
=
9.
Hence we have
Theorem 2 (Gal).
If Q is an Eulerian network or a tree then the value of the search
game with an immobile hider played on Q is
¯
μ
/
2
.
As discussed in Sect.
1.1.1
of Chap.
1
, the RCPT is not optimal for all networks,
in particular the 3-arc network depicted in Fig.
1.1
, though this was not shown for
another 15 years [
15
].
2.4 Weakly Cyclic and Weakly Eulerian Networks
Solutions of the game described in the previous section are not limited to trees and
Eulerian networks. In [
17
] Reijnierse and Potters solve the game for
weakly cyclic
networks, showing that the RCPT is optimal for the searcher, so that the value is
¯
2. A weakly cyclic network can be thought of as a tree network for which some of
the nodes have been replaced with cycles. Alternatively, a weakly cyclic network can
be defined more precisely as a network for which there are at most two disjoint paths
between any two nodes. Weakly cyclic networks cannot contain any subnetwork
μ
/
Search WWH ::

Custom Search