Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
This initial position on the trajectory is denoted
v
=
−
1, the position when predator
and prey are closest is position
v
0, and the position when the predator is again
at distance
r
from the prey, and it is assumed that the potential encounter finishes,
is position
v
=
=
1. The length of the trajectory is 2
r
cos
θ
and the minimum distance
between predator and prey (occurring when
v
. At any position
v
on the
trajectory, the distance between predator and prey can be found by simple triangular
geometry, see Fig.
15.1
.
=
0) is
r
sin
θ
Parameter
Meaning
r
The maximum distance at which prey can detect predators
θ
The angle between the predator's trajectory and the prey direction
s
The speed of movement of the predator prior to an attack
d
(
v
)
The distance from predator to prey when the predator is at position v
Δ
The distance advantage the prey gets from initiating a chase itself
t
The time taken by the predator to reach position
v
f
(
d
)
The probability of the predator catching the prey from distance
d
g
(
d
)
The rate that the predator detects the prey at distance
d
A
(
v
)
The probability that the prey has been detected by position
v
c
The multiplicative cost of surviving through outrunning a predator
Table 15.1
The parameters for the model of Broom and Ruxton [
2
]
a
b
c
1
1
1
b
P
c
P
P
0
0
0
a
d
d
v
v
r
-1
-1
-1
Fig. 15.1
The prey hides at point
P
.(
a
) The interaction begins when the predator enters the area at
point
v
to the most direct route
to the prey. (
b
) The distance
d
of the predator from the prey at point
v
follows from Pythagoras'
theorem using the distances
a
and
c
, with distances
a
=
−
1, at distance
r
from the prey, moving in a direction at an angle
θ
=
vr
cos
θ
,
b
=
r
cos
θ
,
c
=
r
sin
θ
.(
c
)Ifthe
prey flees, it gains an extra distance
Δ
ahead of the predator in the pursuit
Detection of the prey occurs at rate
g
(
d
(
v
))
, and the probability that the prey has
been detected by position
v
is denoted by
A
. Note that the rate of detection is
independent of the speed of the predator, but this speed still affects the probability
of the prey being spotting because it affects how long it will be in range of the prey.
Hence
(
v
)
t
−
(
)=
(
−
(
(
))
)
⇒
1
A
v
ex p
g
d
v
dt
(15.5)
0
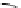






































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search