Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Friction
F= 6
πη
r
Rate of
sedimentation
dx 2r
2
(
ρ
2
-
ρ
)g
dy 9
η
x
=
½
Gravity
RTt
3
πη
rN
A
Brownian
motion
x
=
F = m(1-v
ρ
)g
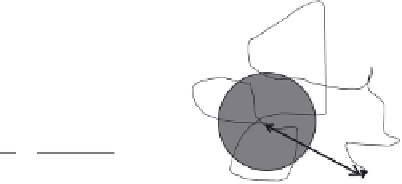
Figure 2.7
The forces of gravity and friction on a suspended particle (left) and the effect
of Brownian motion on a particle's random walk in suspension as a result of collisions with
solvent molecules (right). [r = particle radius,
ρ
= density of particle,
ρ
2
= density of fl uid,
g = acceleration due to gravity,
= viscosity of fl uid, m = mass of particle, v = volume of
particle, R = gas constant, T = temperature, t = time, N
A
= Avogadro's number].
η
Table 2.2
A comparison of calculated diffusion rates (mm/h) for different particle sizes
against the sedimentation rates (mm/h) for some particles of varying density (values given
in brackets gcm
−
3
) suspended in water at room temperature. Note: polyethylene fl oats due
to its low density. Osmium given as an example due to its extreme density.
Particle diameter (nm)
1
10
100
500
Brownian diffusion
1.8635
0.5893
0.1863
0.0833
Polyethylene (0.96)
−
8.82
×
10
−
8
−
8.82
×
10
−
6
−
0.0009
−
0.0220
Polystyrene(1.05)
10
−
7
10
−
5
0.0011
0.0276
1.10
×
1.10
×
Graphite (2.25)
2.76
×
10
−
6
0.0003
0.0276
0.6889
Titania anatase (3.84)
10
−
6
0.0006
0.0626
1.5652
6.26
×
Zinc oxide (5.61)
1.02
×
10
−
5
0.0010
0.1016
2.5407
Cerium (IV) oxide (7.13)
10
−
5
0.0014
0.1351
3.3784
1.35
×
Silver (10.5)
2.09
×
10
−
5
0.0021
0.2094
5.2357
Gold (18.9)
3.94
10
−
5
0.0039
0.3942
9.8541
×
Osmium (22.5)
10
−
5
0.0047
0.4735
11.8381
4.74
×
are constantly bombarded by molecules of the solvent which have an energy related
to the temperature of the system. This means that the particles follow a so-called
random walk. Einstein's law of diffusion shows that the average displacement of a
particle along any given axis in time (t) is proportional to the inverse square root
of the particle radius. This means that the larger the particle the slower it moves
due to Brownian motion. Table 2.2 shows the calculated values for the distances
travelled by diffusion and those travelled due to sedimentation for a range of
materials in water at room temperature. Thus, materials with densities less than
that of the medium in which they are suspended do not sediment under gravity.









Search WWH ::

Custom Search