Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
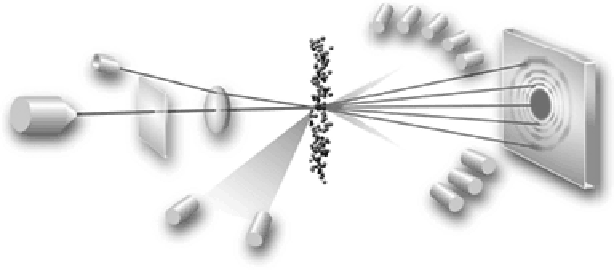
Figure 6.3
Principles of a laser diffraction instruments equipped also with a lower wave-
length laser and additional forward and backscattering detectors to decrease the lower size
limit of the technique. (Reprinted with permission from Malvern Instruments Ltd, UK.)
of
m, and it is thus very suitable to study fl occulation processes. Laser
diffraction measures an equivalent spherical volume diameter (Table 6.2). The
major limitation of laser diffraction for NPs or their agglomerates is the poor
sensitivity and the need for high detection angles for submicron particles.
∼
0.05 - 1000
µ
6.2.3.4
Turbidimetry
Turbidimetry (light transmission measurement) or nephelometry (scattering inten-
sity measurement, typically at a right angle) can be used to measure particle con-
centration in a sample (Irache
et al.
, 1993). Due to the simplicity of measurement
and inexpensive instrumentation turbidimetry is often used in environmental
studies and water quality monitoring (Peng
et al.
, 2002). However, due to the
reasons discussed in Section 6.2.3.2, the scattering intensity depends not only on
particle concentration but also on the size, composition and shape. Consequently,
for anything else than very well defi ned NPs turbidimetry should be used with
caution.
6.2.3.5
Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis
Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) is a recently developed method using track-
ing of the Brownian movement of individual point-scatterers illuminated by a laser
in a fl ow cell under a conventional optical microscope. The detection is recorded
in the microscope by a CCD camera as a high speed movie and the mean squared
displacement between the frames in the sequence is determined for each individual
nanoparticle trajectory. Even though diffusive movement takes place in three
dimensions and the instrument only captures movement in two dimensions, there
is a correction term to the Stokes-Einstein equation to be able to calculate
diffusion coeffi cients or hydrodynamic diameter.
Since the method relies on counting and measuring particles, the obtained size
distributions are number based, compared with the related DLS technique that is
Search WWH ::

Custom Search