Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
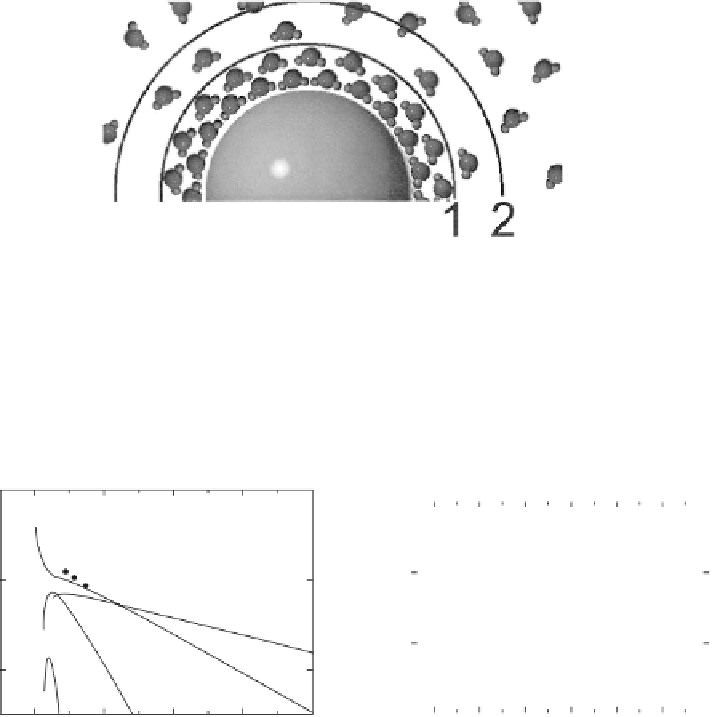
Figure 4.7
Hydration layers around a particle. The density of water molecules around a
surface is highest in the proximity of the surface and decays with distance to the density
observed for water molecules in the bulk solution. This results in several layers of hydration
(1, 2, …. , n). (With kind permission from Springer Science & Business Media:
Reviews in
Environmental Science and Biotechnology
,
1
, 2002, 17-38, A review of non-DLVO interac-
tions in environmental colloidal systems, D. Grasso, K. Subramaniam, M. Butkus, K. Strevett
and J. Bergendahl, Figure 6.)
10
10
pH 10.0
pH 7.0
pH 4.0
pH 3.0
pH 2.58
pH 2.0
DLVO fit
1
1
10
-4
M
0.1
10
-3
M
0.1
10
-1
M
10
-2
M
0.01
0
10
20
30
40
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Distance (nm)
(a)
Distance (nm)
(b)
Figure 4.8
The force F as a function of distance, D: (a) between a silica probe radius
R = 3.5
m and and a fl at silica surface; (b) between a silica glass sphere and a fl at silica
plate as a function of pH. The data points represent the measurements of the surface force
and the solid lines are the best fi t to DLVO theory. ((a) Reprinted by permission from
Macmillan Publishers Ltd,
Nature
,
353
, 239-41, Direct measurement of colloidal forces using
an atomic force microscope, W.A. Ducker, T.J. Senden and R.M. Pashley. Copyright 1991.
(b) Reprinted with permission from W.A. Ducker, T.J. Senden and R.M. Pashley, Measurement
of forces in liquids using a force microscope,
Langmuir
,
8
, 1831-6. Copyright 1992, American
Chemical Society.)
µ
tant at higher ionic strength, owing to adsorbed hydrated cations as shown in Figure
4.8 a (Ducker
et al.
, 1991) and at higher pH conditions due to the higher surface
charge as shown in Figure 4.8b (Ducker
et al.
, 1992 ).
Meagher (1992) measured hydration forces between a silica colloidal sphere
and a silicon sample. It was shown that in 0.01 M CaCl
2
solutions at pH 4.1, the















































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search