Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
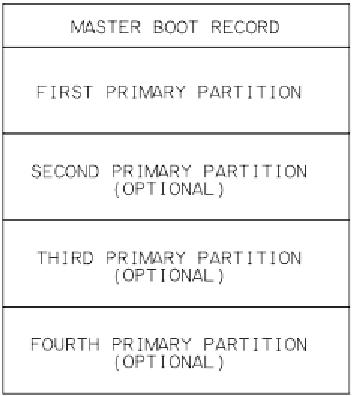
Figure 7-1: Storage media can be formatted with a master boot record and up
to four primary partitions.
add support for capacities and abilities that embedded systems are unlikely
to need. Windows and other operating systems support a variety of file sys-
tems, including options suitable for small embedded systems, so PCs and
embedded systems can access the same media without problems.
Components of Formatted Media
As explained in Chapter 1, bytes in storage media are grouped in blocks
called sectors. All of the sectors in the media have the same capacity, typi-
cally 512. Some file-system drivers support sector sizes that are multiples of
512.
Low-level formatting code allocates most of the sectors to one or more logi-
cal partitions, or volumes. (Figure 7-1) Formatting can be done by a PC, an
embedded system, or another computer that interfaces to the media.
In most storage devices, the first sector in the media (sector zero) is the mas-
ter boot record (MBR) sector. The sector contains an MBR structure, which
in turn contains a partition table that defines the locations of up to four par-
titions. Under Windows, each partition appears as a separate volume, or log-
ical drive with its own drive letter. The MBR sector also has an area that can
Search WWH ::

Custom Search