Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
18.2 RESPIRATORY O
2
REDUCTION CATALYSIS
18.2.1 Basic Aspects of Energy Metabolism
Life requires constant dissipation of energy. This energy comes from the environment,
in the form either of sunlight or of food (reduced organic matter). Respiration is the
most efficient way to extract energy from food [Alberts et al., 2002]. In respiration,
food is ultimately oxidized by an environmental oxidant, such as O
2
in aerobic respir-
ation or a host of other bioavailable oxidants, from nitrate and sulfate to ferric ion
in anaerobic respirations [Moodie and Ingledew, 1990] (Fig. 18.2). Energy metab-
olism is a multistep redox process, starting with food being converted to reduced
electron carriers, such as the reduced forms of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
and flavin adenine dinucleotide (NADH and FADH
2
, respectively), which enter the
respiratory cycle. This cycle proceeds by enzyme-catalyzed electron transfers between
electron carriers of increasing redox potential, from strong reductants such as NADH
Figure 18.2 Summary of respiratory energy flows. Foods are converted into the reduced form
of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH), a strong reductant, which is the most reducing of
the respiratory electron carriers (donors). Respiration can be based on a variety of terminal
oxidants, such as O
2
, nitrate, or fumarate. Of those, O
2
is the strongest, so that aerobic respiration
extracts the largest amount of free energy from a given amount of food. In aerobic respiration,
NADH is not oxidized directly by O
2
; rather, the reaction proceeds through intermediate
electron carriers, such as the quinone/quinol couple and cytochrome c. The most efficient
respiratory pathway is based on oxidation of ferrocytochrome c (Fe
I
cytc
) with O
2
catalyzed by
cytochrome c oxidase (CcO). Of the 550 mV difference between the standard potentials
of cytochrome c and O
2
, CcO converts 450 mV into proton-motive force (see the text for
further details).






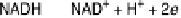



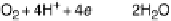






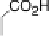
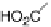
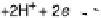
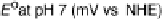













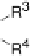
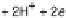



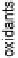


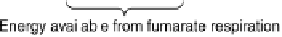
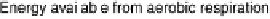
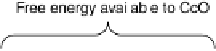































Search WWH ::

Custom Search