Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 11.5 Tafel plots for methanol oxidation on Pt
þ
Ru/C colloid catalysts with different
atomic compositions; at T ¼ 318K: (a) 1.0 M MeOH; (b) 0.1 M MeOH (0.5 M H
2
SO
4
; sweep
rate 1 mV s
21
).
For potentials higher than 0.5 V vs. RHE, the formation of adsorbed oxygen species
at Ru as well as at Pt will block the catalytic surface, leading to a decrease in the metha-
nol adsorption kinetics. Therefore, in a potential range higher than 0.5 V vs. RHE, the
kinetics of methanol oxidation is optimized at a Ru-poor catalyst, because methanol
adsorption is not blocked and because the presence of Ru provides the extra oxygen
atom needed to complete the oxidation of adsorbed CO to CO
2
.
Finally, trimetallic compounds have been developed to enhance the electroactivity
of Pt-based catalysts, for either methanol or ethanol electro-oxidation. A long time
ago, it was reported that adsorption of molybdates (Na
2
MoO
4
) at a Pt black electrode
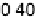
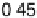
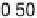
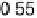




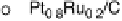



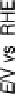


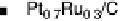
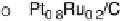




































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search