Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
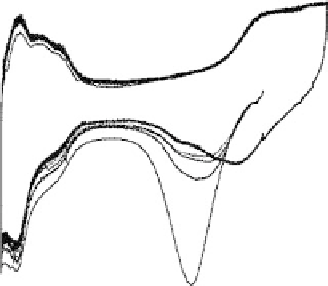
Figure 1.3 Pt catalyst coverage by chemisorbed oxygen species (for Pt/C in a PEFC cathode
at 25 8C): (a) 0.85 V, 3 h of exposure to N
2
,4%O
2
in N
2
and air, and 30 min exposure to O
2
;
(b) 0.95 V, 3 h exposure to N
2
and 30 min exposure to O
2
. From Paik et al. [2004].
Considering the standard potential of 1.23 V associated with Reaction (1.4a), it can be
understood why a dioxygen molecule can be more reactive in the formation of OH
ads
by water oxidation (1.4) than the purely anodic discharge of water driven by a potential
of 0.85 V in an oxygen-free atmosphere. Interestingly, dissociative chemisorption of
O
2
from the gas phase at Pt-group metal surfaces is reported to be strongly accelerated
in the presence of water vapor [Weaver, 2002], suggesting a surface oxidation process
involving dioxygen and surface water molecules, identical or similar to the Reaction
(1.4). As Fig. 1.3 suggests, Reaction (1.4) apparently takes place at cathode potentials

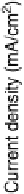









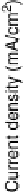




























Search WWH ::

Custom Search