Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
TABLE 9.2 Perdew-Wang (PW91) Binding Energies of O and O
2
on the Pt and
Pt
3
Co Alloy Surfaces. Reprinted with Permission from Xu et al. [2004]
Pt(111)
Pt(111) 22%
Pt skin on Pt
3
Co(111)
Pt
3
Co(111)
Atomic oxygen (eV/O)
I
III
C
P
top
22.49
22.36
22.31 22.28
23.50
n.s.
hcp
23.49
23.28
23.13 23.12
24.02 23.46
fcc
23.88
23.63
23.50 23.20
24.29 23.52
Molecular oxygen (eV/O
2
)
a
b
g
CP
PP
PC
t-b-t
20.62
20.50
20.24 20.34 20.34 20.92 20.53
a
20.65
b
t-f-b
20.61
20.46
n.s.
20.25 20.28 20.92
n.s.
20.77
t-h-b
20.45
20.32
n.s.
n.s.
n.s.
20.67 20.48
n.s.
b-f-b
n.s.
n.s.
n.s.
n.s.
n.s.
n.s.
20.70
n.s.
b-h-b
n.s.
n.s.
n.s.
n.s.
n.s.
n.s.
20.63
n.s.
The binding energies of O and O
2
are referenced to O
(g)
and O
2(g)
, respectively. Surface coverage is 1/4ML
for each species. For comparison, the binding energy of O on Co(0001) is 25.44 eV. The bond energy of a
gas-phase O
2
molecule is 5.64 eV. See Fig. 3.1 for site labeling.
n.s. indicates that the corresponding state is not stable.
remain the reaction centers: those sites that involve a Co atom always bind O and O
2
more strongly than the corresponding Pt-only sites (Table 9.2). O
2
also dissociates
more easily at Co centers, where the transition states of O
2
dissociation are
stabilized and the activation energy is lowered considerably compared with Pt-only
sites of Pt
3
Co(111) or Pt(111) (Fig. 9.11). However, given that the base metal
Figure 9.11 Several minimum energy paths for O
2
dissociation on Pt
3
Co(111) (labeled by respect-
ive initial states), generating
1
2
ML of atomic O, compared with equilibrium and 2% compressed
Pt(111). The points on each path are the “images” or states used to discretize the path with the
climbing-image nudged elastic band method. The zero of the energy axis corresponds to an O
2
molecule and the respective clean surfaces at infinite separation. The points located on the right
vertical axis represent atomic O at
4
ML. (Reproduced with permission from Xu et al. [2004].)



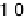

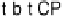

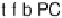


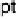


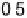

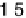

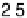


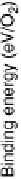
































Search WWH ::

Custom Search